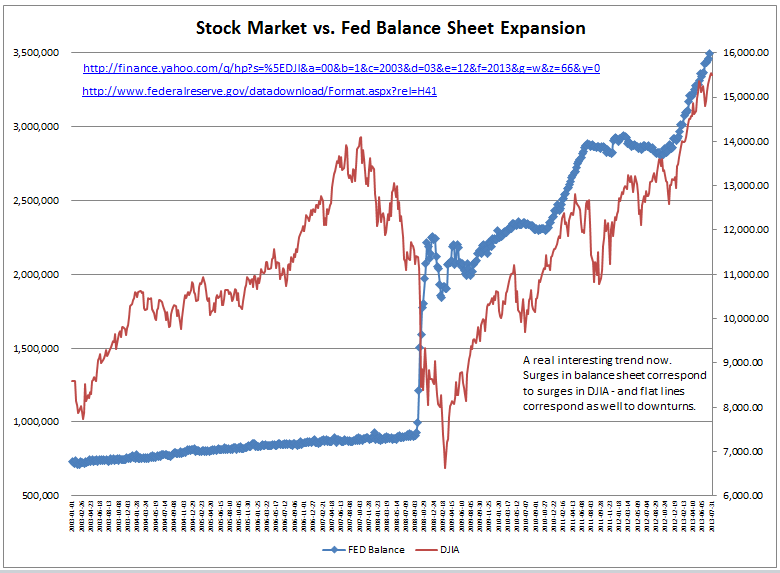
Bonds & Interest Rates
The Half Full Economy
The marginal economic strength that was described in the most recent GDP release from Washington has caused many to double down on their belief that the Federal Reserve will begin tapering Quantitative Easing sometime later this year. While I believe that is a fantasy given our economy’s extreme dependence on QE, market observers should have learned long ago that the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) initial GDP estimates can’t be trusted. A perusal of their subsequent GDP revisions in the last five years reveals a clear trend: They are almost twice as likely to revise initial estimates down rather than up, and the downward adjustments have been much larger on average.
As a result of this phenomenon, an overall optimism has pervaded the economic discussion that has consistently been unfulfilled by actual performance. The government is continuously over promising and under delivering. Unfortunately, no one seems to care.
Measuring the size of the economy accurately in anything close to real time is difficult, inexact, and messy. That is why the BEA has long pursued a policy of initial quarterly estimates (known as the “advanced estimate”), followed by two or three subsequent revisions as more thorough analysis comes to bear. The first estimates come out about a month after the conclusion of a particular quarter. The second and third revisions then come in monthly intervals thereafter. But in the minds of the media, the public and the politicians, the initial report carries much more weight than the revisions. It is the initial report that attracts the screaming headlines and sets the tone. The revisions are typically buried and ignored. This creates an unfortunate situation where the initial estimates are both the most important and the least reliable.
However, logic would dictate that revisions would fall equally in the up and down categories. After all, government bean counters are expected to report objectively, not to create a narrative or manage expectations. If anything, I believe that the public would be better served if they would adhere to the conservative playbook of under promising. That is exactly what they seemed to be doing before the economic crash of 2008. From 2002 to mid-summer 2008, the BEA revised initial GDP estimates a total of 25 times, 80% of which (20 revisions) were higher than their initial estimate. However, the average amplitude of the upward and downward revisions were equal at .5%. The difference may have been a function of the relatively strong economy that the nation saw over that time (which I believe was a result of the unsustainable and artificial housing boom). See the chart below.
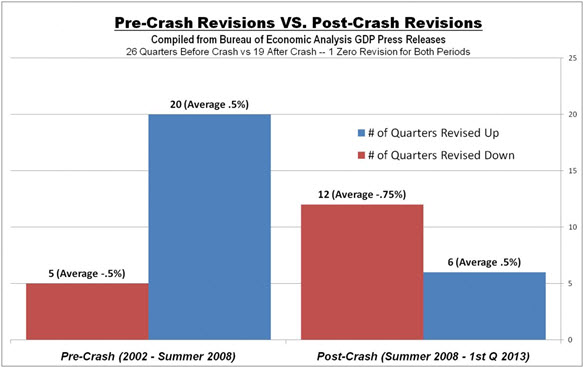
But since mid-2008 we have seen a very different story. 67% of the revisions (12 of 18) have been downward, and those adjustments have been, on average, 50% larger than the upward revisions (.75% vs. .5%). Here’s another way of looking at it: Since mid-2008, revisions have shaved a total of 6 points of growth off the initial estimates. This works out to be an average of 1.3 points of growth per year that some may have expected but that never actually happened.
The pattern of early optimism may stem from the lack of understanding in Washington about how monetary stimulus actually retards economic growth. Many of the statisticians may be former academics who take it as gospel that government spending and money printing create growth. As a result, they expect the initial boost created by stimulus to be sustainable. The evidence suggests that it is not.
But there can be little doubt that these overly optimistic projections have worked wonders on the public relations front. The big Wall Street firms and the talking heads on financial TV set the tone by jumping on the new releases and ignoring the revisions to prior releases. That is precisely what happened last week when the better than expected 1.7% growth in 2nd quarter GDP overshadowed the .7% downward revision to 1st quarter GDP from 1.8% to 1.1%. The initial estimate for 1st quarter GDP, released back in April, was 2.5%. Since the consensus expectation for 2nd quarter GDP was just 1%, the media jumped all over the “good” news, while ignoring the revisions to the prior quarter, and discounting the strong likelihood that Q2 GDP will be revised downward. The nature of our short-term 24-hour news cycle is a big factor in this. Reporters are always looking for the big story of the day, not the minutia of last month. The lack of critical thinking and economic understanding also play a role.
Of course even if you have the discipline to focus on the final estimates, you still aren’t getting the real story. All GDP estimates are based on imperfect inflation measurement tools, which I believe are designed to under report inflation and over report growth. The most recent GDP projection used an annualized .71% inflation deflator to arrive at 1.7% growth. Anyone who believes that inflation is currently running below 1% has simply no grasp of our current economy. Look for more analysis of this topic in my upcoming columns. In the meantime, don’t get excited by initial reports of a healthy recovery. The reality is likely to be more sobering.
Peter Schiff is the CEO and Chief Global Strategist of Euro Pacific Capital, best-selling author and host of syndicated Peter Schiff Show.
Subscribe to Euro Pacific’s Weekly Digest: Receive all commentaries by Peter Schiff, John Browne, and other Euro Pacific commentators delivered to your inbox every Monday!
Don’t forget to sign up for our Global Investor Newsletter.


What is going on in America at least in 2013, is the following summary: of the 953K jobs “created” so far in 2013, only 23%, or 222K, were full-time. Part-time jobs? 731K of the 953K total.
For 2 more disquieting charts & commentary click on this link ZeroHedge
(Source Bureau of Labor Statistics)


Just over a week ago, the probability of a September ‘Taper’ were a mere 14% with the majority of the ‘smart’ money betting on a ‘December 2013 at the earliest’ start to the Fed’s removal of the punchbowl. September 2013 is now the front-runner at a 36% probability, based onPaddyPower’s latest odds. September has surgede from a 7/1 outsider to a 7/4 favorite in that brief time (and October also improved from 11/1 to 7/1). It seems that JPY-carry is well aware of this shift (having surged over 4% in the same period). Between Merkel’s election and the FOMC, the 3rd week of September (which just happens to perfectly correspond to an option expiration) looks set for some fireworks one way or another.
While bonds may well have repriced for this slowing of liquidity delivery, and credit and FX moves signal an awareness that a disturbance in the force is forthcoming, we suspect stocks remain sanguinely oblivious still.

We Can’t Take the Chance
A Few Impossible Things
Thinking About Alternatives
14 Years and Counting
Montana, San Antonio, Chicago, Bismarck, Denver, Toronto, NYC…
 What would it have been like to be in the decision-maker’s seat at a central bank in the midst of the crisis in 2008-09? You’d know that you won’t have the luxury of going back and making better decisions five years later. Instead, you have to act on the torrent of information that’s coming at you from every quarter, and none of it is good. Major banks are literally collapsing, the interbank market is almost nonexistent, and there is panic in the air. Perhaps you feel that panic in the pit of your stomach. This week we’ll perform a little thought experiment to see if we can extrapolate what is likely to happen in when the next crisis kicks in.
What would it have been like to be in the decision-maker’s seat at a central bank in the midst of the crisis in 2008-09? You’d know that you won’t have the luxury of going back and making better decisions five years later. Instead, you have to act on the torrent of information that’s coming at you from every quarter, and none of it is good. Major banks are literally collapsing, the interbank market is almost nonexistent, and there is panic in the air. Perhaps you feel that panic in the pit of your stomach. This week we’ll perform a little thought experiment to see if we can extrapolate what is likely to happen in when the next crisis kicks in.
This week’s letter was triggered by a semiformal debate in Maine last week. David Kotok assembled about 50 economists, financial analysts, money managers, and media personalities to share a few days of fabulous food, what turned out to be great fishing, and awesome conversation. There were more Federal Reserve economists this year than in the past, as well as more attendees with the title “Chief Economist” on their business cards, many from large institutional names you would recognize. This was my seventh year to attend “Camp Kotok.” David really did a marvelous job of bringing a diverse group of thinkers together, and I think everyone agreed this was the best conference ever. I learned a lot.
Before we get into the letter, a little side note. Luciana Lopez from Reuters attended for the first time this year and wanted to do interviews. David asked me if I would take her out on the lake in our boat, since most of the other attendees went out in small canoes. Trey and I were glad to share our space. While we were out fishing, she asked if she could interview me. I said “Sure” and waited for her to bring out her recorder. She pulled out an iPhone 5 and started asking questions. Not the usual studio setting I am used to. I had serious trepidations about how this was going to look on-screen.
She sent a link to her edited interviews last Monday, and I have to admit I was impressed at what she could do with a simple iPhone 5. I am supposed to be on top of a changing world, but sometimes these things still take me by surprise. I make no representations about the quality of the content of the interviews, at least my portion of them, but the phone is another matter. And in a few years this will be a $100 consumer item.
In her interviews, Luciana asked two questions: “When will the Fed start to taper?” and “Who will be the next Fed chair?” You can see some of our answers at reut.rs/13if7Er and reut.rs/13gegE8.
We Can’t Take the Chance
On Saturday night David scheduled a formal debate between bond maven Jim Bianco and former Bank of England Monetary Policy Committee member David Blanchflower (everyone at the camp called him Danny). Jim Bianco needs little introduction to longtime readers, but for newbies, he is one of the top bond and interest-rate gurus in the world. His research is some of the best you can get – if you can get your hands on it.
Blanchflower needs a little setup. He is currently a professor at Dartmouth and has one of the more impressive resumés you will find. He is not afraid to be a contrarian and voted in the minority in 18 out of 36 meetings in which he participated as an external member of the Bank of England‘s interest rate-setting Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) from June 2006 to June 2009. (The MPC is the British equivalent of the US Federal Open Market Committee.) Blanchflower’s The Wage Curve, drawing on 8 years of data from 4 million people in 16 countries, argued that the wage curve, which plots wages against unemployment, is negatively sloping, reversing the conclusion from generations of macroeconomic theory. “The Phillips Curve is wrong, it’s as fundamental as that,” Blanchflower has stated. Blanchflower is also known as the “happiness guru” for his work on the economics of happiness. He quantified the relationship between age and happiness and between marriage, sex, and happiness. Who knew that people who have more sex are happier? Well, we all did, but now we have economic proof.
I got to spend a good deal of time with Danny on this trip and enjoyed hearing him talk about what it was like to be responsible for setting monetary policy in the midst of a crisis. We also argued late into the night on a variety of subjects. He is an altogether fun guy as well as a professional who takes his economics seriously. He is far more mainstream than your humble analyst, as were many of the denizens of Camp Kotok. On the other hand, I can’t think of a major stream of economic thought that wasn’t represented aggressively at one point or another. If you have thin skin or weak data, this outing is one you might not enjoy. You need to bring your A game with this crowd.
The format for the debate between Bianco and Blanchflower was simple. The question revolved around Federal Reserve policy and what the Fed should do today. To taper or not to taper? In fact, should they even entertain further quantitative easing? Bianco made the case that quantitative easing has become the problem rather than the solution. Blanchflower argued that quantitative easing is the correct policy. Fairly standard arguments from both sides but well-reasoned and well-presented.
It was during the question-and-answer period that my interest was piqued. Bianco had made a forceful argument that big banks should have been allowed to fail rather than being bailed out. The question from the floor to Danny was, in essence, “What if the Bianco is right? Wouldn’t it have been better to let banks fail and then restructure them in bankruptcy? Wouldn’t we have recovered faster, rather than suffering in the slow-growth, high-unemployment world where we find ourselves now?”
Blanchflower pointed his finger right at Jim and spoke forcefully. “It wasn’t the possibility that he was right that preoccupied us. We couldn’t take the chance that he was wrong. If he was wrong and we did nothing, the world would’ve ended and it would’ve been our fault. We had to act.”
That sentence has stayed with me for the past week: “We couldn’t take the chance that he was wrong.” Whether or not you like the implications of what he said, the simple fact is that he was expressing the reigning paradigm of economic thought in the world of central bankers.
Now, let’s hold that train of thought for a few minutes as we introduce an essay by French geophysicist and complex systems analyst Didier Sornette and his colleague Peter Cauwels. Sornette is Professor on the Chair of Entrepreneurial Risks at the Department of Management Technology and Economics of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich. (This introduction comes from work I have been doing in collaboration with Jonathan Tepper, my co-author for Endgame.)
By far the biggest advances in understanding the dynamics of bubbles in recent years have come from Sornette. He has developed mathematical models to explain earthquake activity, Amazon book sales, herding behavior in social networks like Facebook, and even stock market bubbles and crashes. He wrote a book titled Why Stockmarkets Crash. He found that most theories do a very poor job of explaining bubbles.
Sornette found that log-periodic power laws do a good job of describing speculative bubbles, with very few exceptions. Classic bubbles tend to have a parabolic advances with shallow and increasingly frequent corrections. Eventually, you begin to see price spikes at one-day, one-hour, and even ten-minute intervals before crashes.
After a crash, journalists go looking for the cause. They’ll blame something like portfolio insurance for the crash of 1987 or the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers for the Great Recession, rather than blaming a fundamentally unstable market. Sornette disagrees:
Most approaches to explain crashes search for possible mechanisms or effects that operate at very short time scales (hours, days or weeks at most). We propose here a radically different view: the underlying cause of the crash must be searched months and years before it, in the progressive increasing build-up of market cooperativity or effective interactions between investors, often translated into accelerating ascent of the market price (the bubble). According to this “critical” point of view, the specific manner by which prices collapsed is not the most important problem: a crash occurs because the market has entered an unstable phase and any small disturbance or process may have triggered the instability. Think of a ruler held up vertically on your finger: this very unstable position will lead eventually to its collapse, as a result of a small (or absence of adequate) motion of your hand…. The collapse is fundamentally due to the unstable position; the instantaneous cause of the collapse is secondary. In the same vein, the growth of the sensitivity and the growing instability of the market close to such a critical point might explain why attempts to unravel the local origin of the crash have been so diverse. Essentially, anything would work once the system is ripe.
Sornette’s conclusion is that a fundamentally unstable economic system plus human greed means that market bubbles and crashes won’t disappear anytime soon.”
A Few Impossible Things
I want to focus on the recent paper Sornette wrote with Cauwels, entitled “The Illusion of the Perpetual Money Machine.” I’m going to quote a few paragraphs from the introduction. They begin with that marvelous exchange from Alice in Wonderland:
There is no use trying,” said Alice. “One can’t believe impossible things.”
“I daresay you haven’t had much practice,” said the Queen. “When I was your age, I always did it for half an hour a day. Why, sometimes I’ve believed as many as six impossible things before breakfast.”
– Lewis Carroll
Chasing fantasies is not the exclusive pastime of little girls in fairy tales. History is speckled with colorful stories of distinguished scientists and highly motivated inventors pursuing the holy grail of technology: the construction of a perpetual motion machine. These are stories of eccentric boys with flashy toys, dreaming of the fame and wealth that would reward the invention of the ultimate gizmo, a machine that can operate without depleting any power source, thereby solving forever our energy problems. In the mid-1800s, thermodynamics provided the formal basis on what common sense informs us: it is not possible to create energy out of nothing. It can be extracted from wood, gas, oil or even human work as was done for most of human history, but there are no inexhaustible sources.
What about wealth? Can it be created out of thin air? Surely, a central bank can print crispy banknotes and, by means of the modern electronic equivalent, easily add another zero to its balance sheet. But what is the deeper meaning of this money creation? Does it create real value? Common sense and Austrian economists in particular would argue that money creation outpacing real demand is a recipe for inflation. In this piece, we show that the question is much more subtle and interesting, especially for understanding the extraordinary developments since 2007. While it is true that, like energy, wealth cannot be created out of thin air, there is a fundamental difference: whereas the belief of some marginal scientists in a perpetual motion machine had essentially no impact, its financial equivalent has been the hidden cause behind the current economic impasse.
The Czech economist Tomáš Sedláček argues that, while we can understand old economic thinking from ancient myths, we can also learn a lot about contemporary myths from modern economic thinking. A case in point is the myth, developed in the last thirty years, of an eternal economic growth, based in financial innovations, rather than on real productivity gains strongly rooted in better management, improved design, and fueled by innovation and creativity. This has created an illusion that value can be extracted out of nothing; the mythical story of the perpetual money machine, dreamed up before breakfast.
To put things in perspective, we have to go back to the post-WWII era. It was characterized by 25 years of reconstruction and a third industrial revolution, which introduced computers, robots and the Internet. New infrastructure, innovation and technology led to a continuous increase in productivity. In that period, the financial sphere grew in balance with the real economy. In the 1970s, when the Bretton Woods system was terminated and the oil and inflation shocks hit the markets, business productivity stalled and economic growth became essentially dependent on consumption. Since the 1980s, consumption became increasingly funded by smaller savings, booming financial profits, wealth extracted from house prices appreciation and explosive debt. This was further supported by a climate of deregulation and a massive growth in financial derivatives designed to spread and diversify the risks globally.
The result was a succession of bubbles and crashes: the worldwide stock market bubble and great crash of 19 October 1987, the savings and loans crisis of the 1980s, the burst in 1991 of the enormous Japanese real estate and stock market bubbles and its ensuing “lost decades”, the emerging markets bubbles and crashes in 1994 and 1997, the LTCM crisis of 1998, the dotcom bubble bursting in 2000, the recent house price bubble, the financialization bubble via special investment vehicles, speckled with acronyms like CDO, RMBS, CDS, … the stock market bubble, the commodity and oil bubbles and the debt bubbles, all developing jointly and feeding on each other, until the climax of 2008, which brought our financial system close to collapse.
Each excess was felt to be “solved” by measures that in fact fueled following excesses; each crash was fought by an accommodative monetary policy, sowing the seeds for new bubbles and future crashes. Not only are crashes not any more mysterious, but the present crisis and stalling economy, also called the Great Recession, have clear origins, namely in the delusionary belief in the merits of policies based on a “perpetual money machine” type of thinking.
The problems that we have created cannot be solved at the level of thinking we were at when we created them.” This quote attributed to Albert Einstein resonates with the universally accepted solution of paradoxes encountered in the field of mathematical logic, when the framework has to be enlarged to get out of undecidable statements or fallacies. But, the policies implemented since 2008, with ultra-low interest rates, quantitative easing and other financial alchemical gesticulations, are essentially following the pattern of the last thirty years, namely the financialization of real problems plaguing the real economy. Rather than still hoping that real wealth will come out of money creation, an illusion also found in the current management of the on-going European sovereign and banking crises, we need fundamentally new ways of thinking.”
And with that biting critique of central bank policy making, we come back to Blanchflower’s fateful line: “We couldn’t take the chance that he was wrong.”
Without a fundamental shift in economic thought at the highest levels of central banking, there is little doubt that the response of any central bank during the next crisis – and there will always be a next crisis – will be more the same. Central banks will again apply the limited tools they have: low interest rates, quantitative easing, a variety of bailout mechanisms – in short, they will resort to the financial repression of savers in the name of the greater good.
Jim Bianco can argue, far more eloquently than your humble analyst, that savers should be rewarded, not punished; that financial repression should only be practiced in extremis; and that moral hazard should be respected. But the reality is that the people with their hands on the levers simply believe with all their hearts in a different theoretical economic framework and will not take a chance on being wrong. They will act just as they have in the past.
I would argue, and I think Sornette would agree, that the current policies are simply increasing the instability of the entire system, leading up to another major dislocation in the not-too-distant future. In much the same way that everyone loved rising house prices in the middle of the last decade, we all find contentment in a rising stock market now. For Bernanke and his kin, the markets simply confirm the correctness of their policies. “More cowbell!” is the economic order of the day.
As Sornette put it, “Each excess was felt to be ‘solved’ by measures that in fact fueled following excesses; each crash was fought by an accommodative monetary policy, sowing the seeds for new bubbles and future crashes.”
Richard Fisher, Dallas Federal Reserve President, has been arguing forcefully that the Fed needs to begin tapering its quantitative easing. He is part of a growing chorus that is increasingly uncomfortable with the potential unintended consequences of massive accommodation and the financial repression of savers. Let us hope they are gaining a hearing.
Thinking About Alternatives
Last week I started my letter with a simple but vehement question: “What in the world is going on?!” In seeking an answer to that question, we examined some data points in the market and highlighted the idea of diversifying into alternative investment strategies as a means of balancing our portfolios during this precarious period. This week I want to follow up that discussion with a note on an important topic with regard to evaluating alternative investment funds: manager selection and the concept of performance dispersion.
In the alternative investment arena, a manager’s efforts to deliver higher, risk-adjusted returns can produce huge returns … or significant losses. Therefore, performance dispersion – the difference between the best- and worst-performing funds can be quite large. To avoid finding themselves toward the bottom of that spread, investors should select a fund manager carefully
My partners at Altegris have produced a timely strategy paper titled “All Managers Are Not Created Equal” that illustrates why manager selection is such an important part of the alternative investment process. Written by my good friend Jon Sundt, President and CEO of Altegris, the piece does a great job of covering both the opportunities and the challenges presented to investors when they choose an alternative investment manager. I encourage you to download and study this paper in detail if you are looking to diversify into alternative investments.
14 Years and Counting
It was 14 years ago this week that I began publishing Thoughts from the Frontline on the internet, on a more or less weekly basis. All the letters from January 2001 on – the good, the bad, and the embarrassing – can be found in the archives at http://www.mauldineconomics.com. That is close to 7000 pages of commentary, some of which I’m proud of and some of which I’d like to bury in the deepest, darkest parts of the internet. Together, you and I have gone through recessions, bull and bear markets, credit crises, and several bubbles, and we have examined at least 100 different topics.
I started with 2,000 email addresses and must admit I never thought at the beginning that I would attract such a wide audience. We will be doing another survey soon, but the past surveys have shown that about 25% of you live outside of the United States. The majority of you are very well-educated and reasonably affluent; but in a list as large as this we go from people who are self-educated or just beginning their education to PhDs and people with immense experience, and from people who are just beginning to accumulate net worth to a few readers who have already amassed billions. I’ve had the pleasure of meeting many of you and corresponding with many more over the years. I am constantly amazed at the thoughtfulness and diversity of my readers, but the one constant seems to be that you are genuinely nice people. I look at the comments section on other writers’ sites and compare them with the notes from my own readers, and it is obvious that you are a cut above the usual crowd. I am humbled by your support and proud of you as well. I am fully aware that the highest compliment any writer can receive is an allocation of time from his readers. I am truly grateful for being allowed to be part of your life.
My business model has changed over the years, and we anticipate a few more changes at Mauldin Economics in the coming year, all in the effort to serve you better. The one thing that will not change is this letter and my companion letter, Outside the Box. I will still write these every week, and they will remain free. You will continue to get my unvarnished opinions, the most interesting essays I can find, and the best macroeconomic guidance I can muster. When I began writing this letter, my prime motive was to help us all understand how the puzzle pieces fit together. That goal has not changed in 14 years. The puzzle seems to have gotten more complicated, so we have an even greater need today to assemble the jumble of pieces into a coherent picture.
Let me thank you from the bottom of my heart for being one of my readers. While it may sound a little corny, I have always thought of each of you as one of my closest friends. That is the way I approach writing the letter, much as if you and I were sitting at a corner table having a quiet conversation, informal yet intense, and animated with a sense of fun and the anticipation of discovery.
Here’s to another 14 years of continued conversation.
Montana, San Antonio, Chicago, Bismarck, Denver, Toronto, NYC…
The list above sounds like a lot of travel, but somehow I am not gone that many days. I will be in Montana this week for R&R with my friend Darrell Cain at his home on Flathead Lake. I’ll catch up on some reading and have some well-deserved rest, as I have just finished a major project that we will announce in a few months. As those around me know, I’ve been consumed by projects the past few months and am ready for a more normal life. Montana sounds perfect at the moment.
The weekend before Labor Day, I will be in San Antonio for the 71st World Science Fiction Convention, Lone Star Con 3, where I will get to hang out with some of my favorite writers and talk about both history and the future with guys who live in the past and the future (ignoring the present). I have never been to one of these, and the experience has long been on my bucket list.
Then I will be off to Chicago for a presentation (details to follow next week) and after that on to Bismarck, North Dakota, for a few days with BNC National Bank. Lacy Hunt will join me for an all-day conference with their clients, and I am pretty sure it will be open to the public. I’ll also get an update from BNC and Loren Kopseng on the Bakken oil boom. If the stars line up right, I will take an extra day and fly down with my friend Loren to South Dakota. If that works out, I will be able to say I have been in all 50 states.
The next week I fly to Denver for a day to be with the team at Altegris Investments (details to follow), and then that next weekend I fly to Toronto to be with Louis Gave of GaveKal. There will be a seminar on Monday morning, Aug. 23rd. If you would like to attend, you can register at http://gavekal.com/seminar.cfm or contactclightbound@gavekal.com“>Chris Lightbound with any questions. From Denver I will fly on to New York City for a few days for media and meetings. While that schedule may seem busy, it involves only about 10 nights away from home for the month, which is less than half of what I’ve been doing for the last year. I guess it’s all relative.
And speaking of anniversaries, this week marks two years of not drinking. I can’t say that I don’t miss Chardonnays, but I value my health more. As Clint Eastwood said, “A man’s got to know his limitations.” I am seeing a lot of spectacular advances in the biotechnology world that we at Mauldin Economics will be writing about in the next few months, but I haven’t yet come across a company with a pill that will let me metabolize alcohol with no ill effects on my body so that I can just enjoy the taste of the wine. Contrary to company policy, when I find that company I will probably invest in it first and then tell you about it. Just saying…
Have a great week and enjoy your summer. I see a weekend with kids and family and last-minute work on the big project I mentioned. But it’s all good.
Your amazed at how it’s all turned out analyst,
John Mauldin
Category: Think Tank
Sign Up
Register now to access free Mauldin Economics newsletters online, post comments to articles, as well as access your paid subscriptions.
It’s quick and easy just enter your information – Registration is FREE!
Share Your Thoughts on This Article

Reflections on “Paper Reserves” of Central Banks; Gold and the Tapering Disconnect
But what about foreign central bank assets, especially China and Japan?
Reflections on “Paper Reserves” of Central Banks
Hugo Salinas Prices covers the topic in an excellent article Some Thoughts on ‘International Reserves’
International reserves, excluding gold, as reported by Bloomberg, courtesy of Doug Noland at www.prudentbear.com on July 26, 2013, stood at $11.167 Trillion dollars.
International reserves, excluding gold, are mainly made up of dollar and euro holdings.
On August 1, 2011, holdings amounted to $10.063 Trillion dollars. One year later, holdings had increased to $10.450 Trillion dollars, an increase of $387 billion dollars.
In the most recent twelve months, holdings have increased by $717 billion dollars, to the present level of $11.167 Trillion dollars.
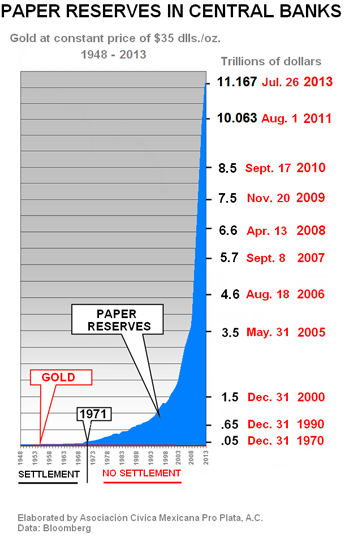
International reserves increase when importing countries cannot pay for their imports with exports; in other words, when the importing countries have “trade imbalances” and make up the trade imbalance by sending (mainly) either dollars or euros to the exporting countries.
The increase in “International Reserves Excluding Gold” from 1971 to the present – 42 years – has been spectacular.
It is important to note that “International Reserves” are invested in diverse Bonds, prima facie evidence that trade imbalances have not been settled since 1971. Settlement happens when a debt is paid. If a country owns Bonds, it is a holder of debt and has not been paid. Had the trade imbalances been settled, International Reserves would be not much different from what they were in 1971.
“International Reserves” thus represent credit which the exporting countries of the world have granted to the importing countries which use dollars and euros as money; when these countries tender dollars or euros in “payment”, they are not settling any debt; they are simply running up more debts with the exporting countries. $11.167 Trillion dollars and counting. The Reserves earn interest – they are invested in Bonds – and so the Reserves must also grow, as interest earned accumulates.
When and how will this increase in the debt of the importing countries to the exporting countries find a limit?
10 days, 10 weeks, 10 months, 10 years – nobody knows. But this game is going to end, someday, and its ending will be painful. When the dust settles, a whole new world will replace the present one. We have no idea what it will look like, but it will be here, populated by humanity who will not cease to wonder: “What were they thinking?”
Gold and the Tapering Disconnect
It should be crystal clear this “game” cannot possibly continue forever. Yet, the doves on the Fed, notably Janet Yellen (who amazingly is even more dovish than Bernanke), act and talk as if it can.
Is any “tapering” is going to occur? Certainly the Fed is not going to hike rates, even if some small amount of tapering does occur.
This setup should be good for gold, but it sure hasn’t.
Curiously, the stock market acts as if no tapering is coming, but gold acts as if the Fed is actually about to tighten, not just taper.
As with perpetually rising trade deficits, this disconnect will not go on forever, but I cannot say when it ends, and nor can anyone else.
For more on the balance of trade problem and how to permanently fix it, please see Hugo Salinas Price and Michael Pettis on the Trade Imbalance Dilemma; Gold’s Honest Discipline Revisited.
Mike “Mish” Shedlock
http://globaleconomicanalysis.blogspot.com
Read more at http://globaleconomicanalysis.blogspot.com/2013/08/reflections-on-paper-reserves-of.html#akDpoy3qUXx0Ammm.99