Bonds & Interest Rates
After nailing the recent peak in rising yields, Gary Tanashian takes a look at where we are likely going intermediate term from here – R Zurrer for Money Talks
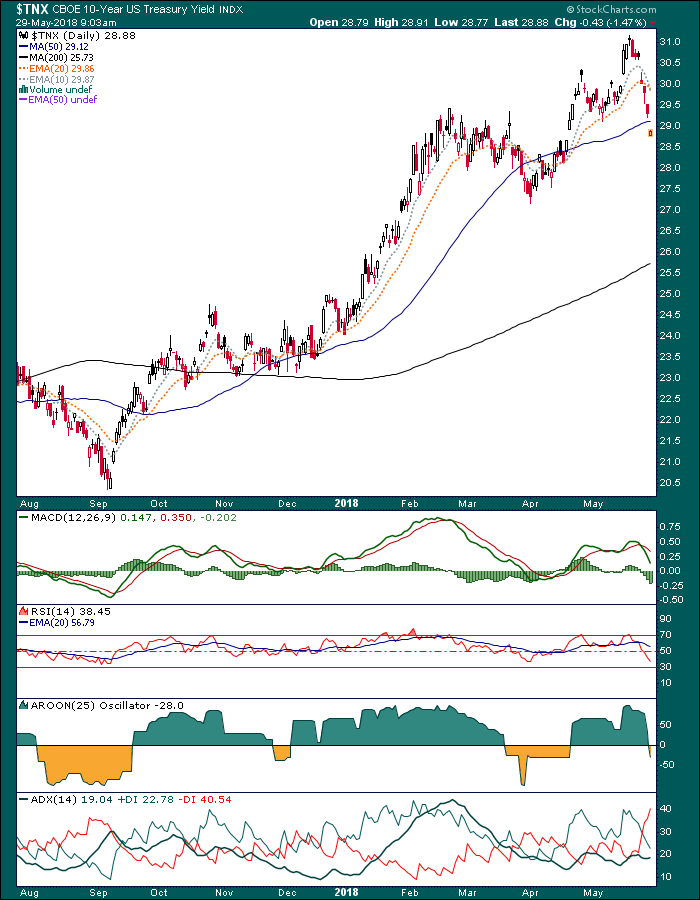
It was just a little over a week ago (May 20) that NFTRH 500 presented a case for caution on the rising bond yields tout that was vigorously in play across the financial media. Here is an excerpt from the Bond Market Sentiment segment presented at the time.
From this public post:
I want to make clear that I am not trying to predict anything. I am simply trying not to have people (myself included) running like stupid lemmings (do lemmings run, waddle or put themselves in motion in some other way?) over a media-obscured cliff.
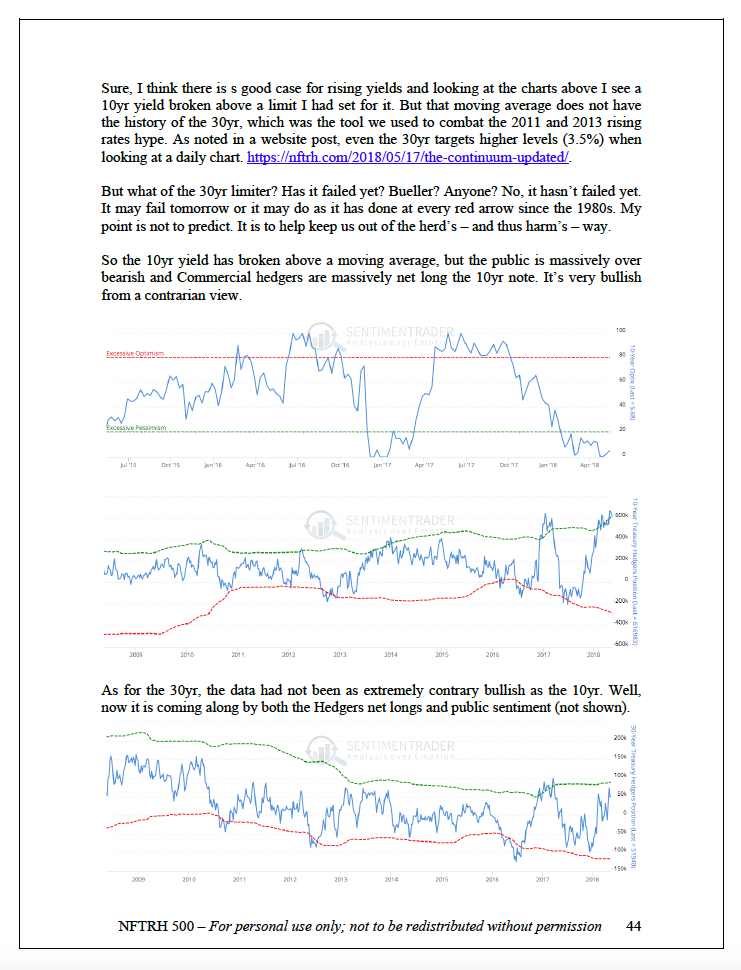
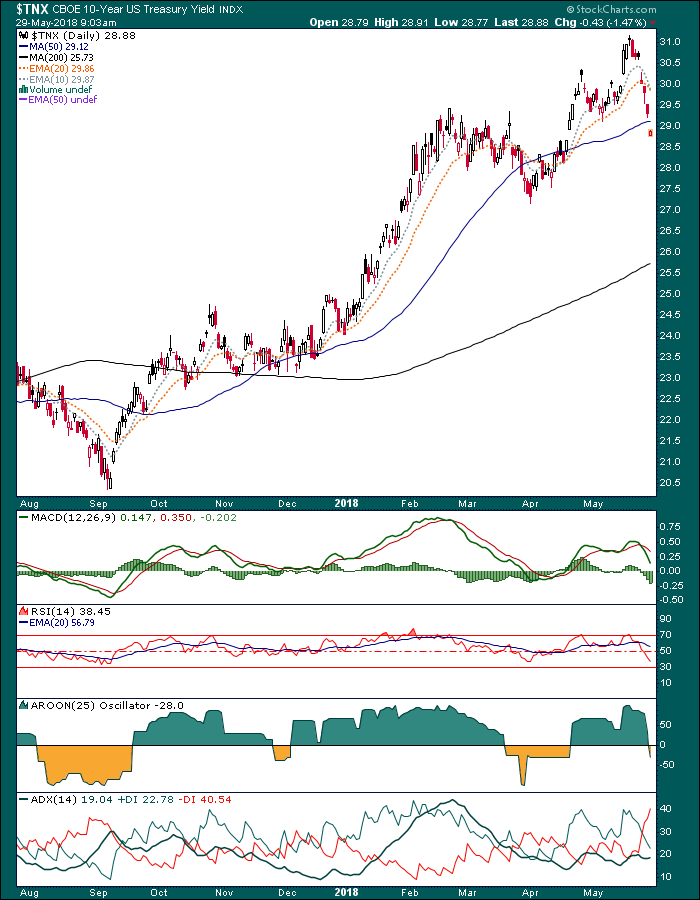
So today here we are, with the 10 year yield having dropped from the cacophony-inducing 3.1% level and I wish to announce that I am not making fun of the bond gurus anymore because the froth has been skimmed off and the intermediate trend in yields is bullish, not bearish.
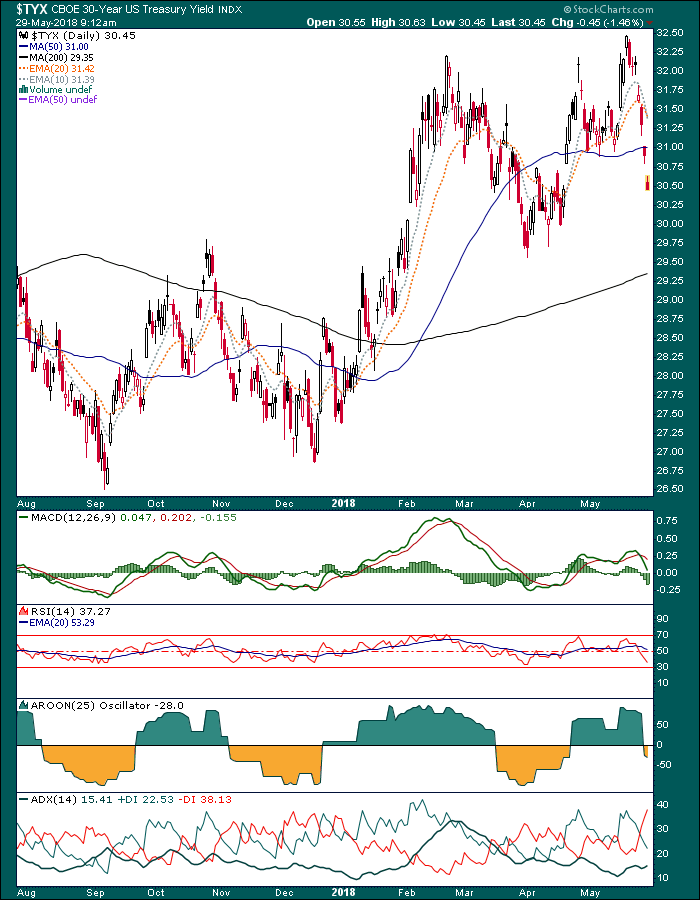
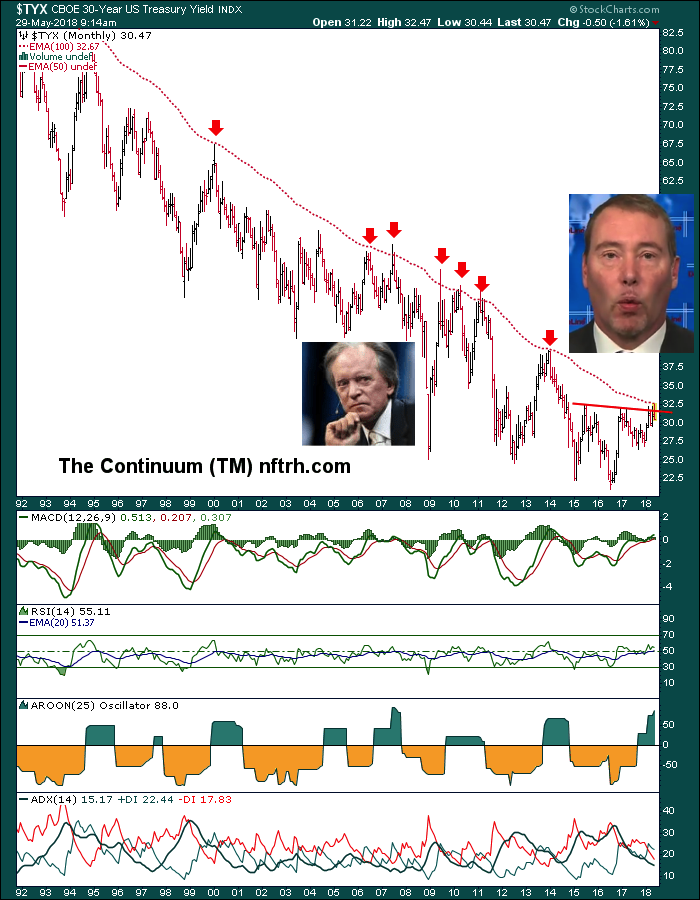
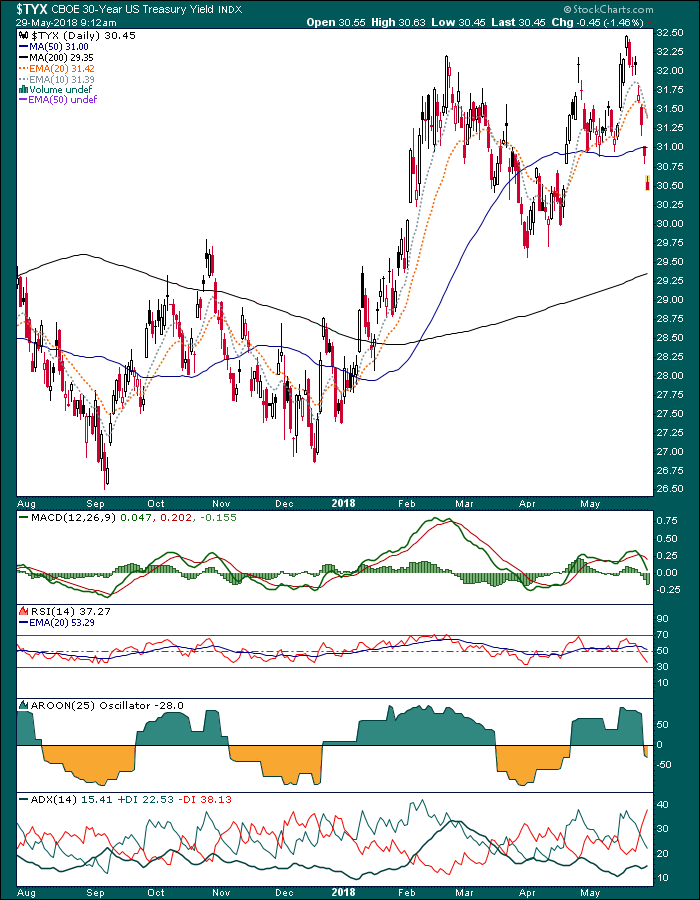
The 30 year is even more soundly corrected.
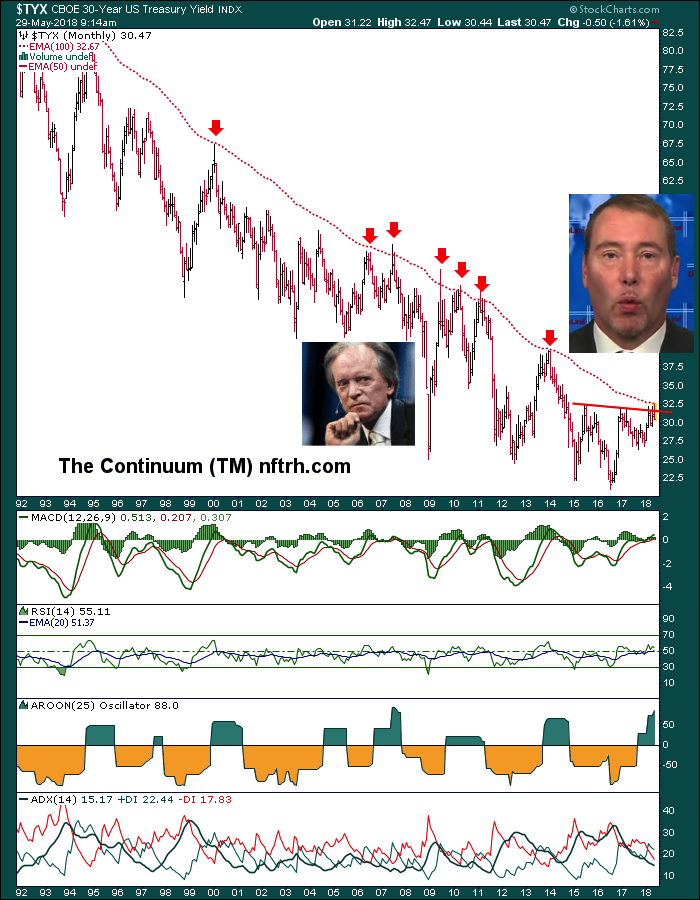
also from Gary:
GOLD, US STOCKS AND BONDS
John Mauldin focuses in on businesscycles, his theories that economic cycles have been replaced with credit cycles, that a tech bubble will eventually spark a recession and that financial market fireworks aren’t far away – R Zurrer for Money Talks
Cycling Economies
Corporate Debt Disaster
Blowing the Whistle
My Writing Productivity Secret
Chicago, Orange County, Raleigh
In last week’s letter, I mentioned an insightful comment my friend Peter Boockvar made at dinner in New York: “We now have credit cycles instead of economic cycles.” That one sentence provoked numerous phone calls and emails, all seeking elaboration. What did Peter mean by that statement?
I vividly remembered that quote because it resonated with me. I’ve been saying for some time that the next financial crisis will bring a major debt crisis. But as you’ll see today, it is a small part, maybe the opening event, of a rapidly-approaching train wreck. We’ll need several weeks to tease out all the causes and consequences, so this letter will be the first in a series. These will be some of the most important letters I’ve ever written. Something is on the tracks ahead and I don’t see how we’ll avoid hitting it. So, read these next few letters carefully.
First, a reminder that today is the deadline to sign up for Over My Shoulder to get the special welcome package we set up for you and a guarantee your $9.95 monthly subscription fee will never go up.
Now, let’s talk about the coming train crash.
Cycling Economies
In 1999, I began saying the tech bubble would eventually spark a recession. Timing was unclear because stock bubbles can blow way bigger than we can imagine. Then the yield curve inverted, and I said recession was certain. I was early in that call, but it happened.
In late 2006, I began highlighting the subprime crisis, and subsequently the yield curve again inverted, necessitating another recession call. Again, I was early, but you see the pattern.
Now let’s fast-forward to today. Here’s what I said last week that drew so much interest.
Peter [Boockvar] made an extraordinarily cogent comment that I’m going to use from now on: “We no longer have business cycles, we have creditcycles.”
For those who don’t know Peter, he is the CIO of Bleakley Advisory Group and editor of the excellent Boock Report. Let’s cut that small but meaty sound bite into pieces.
What do we mean by “business cycle,” exactly? Well, it looks something like this:
Photo: Wikispaces (Creative Commons license)
A growing economy peaks, contracts to a trough (what we call “recession”), recovers to enter prosperity, and hits a higher peak. Then the process repeats. The economy is always in either expansion or contraction.
Economists disagree on the details of all this. Wikipedia has a good overview of the various perspectives, if you want to geek out. The high-level question is why economies must cycle at all. Why can’t we have steady growth all the time? Answers vary. Whatever it is, periodically something derails growth and something else restarts it.
This pattern broke down in the last decade. We had an especially painful contraction followed by an extraordinarily weak expansion. GDP growth should reach 5% in the recovery and prosperity phases, not the 2% we have seen. Peter blames the Federal Reserve’s artificially low interest rates. Here’s how he put it in an April 18 letter to his subscribers.
To me, it is a very simple message being sent. We must understand that we no longer have economic cycles. We have credit cycles that ebb and flow with monetary policy. After all, when the Fed cuts rates to extremes, its only function is to encourage the rest of us to borrow a lot of money and we seem to have been very good at that. Thus, in reverse, when rates are being raised, when liquidity rolls away, it discourages us from taking on more debt. We don’t save enough.
This goes back farther than 2008. The Greenspan Fed pushed rates abnormally low in the late 1990s even though the then-booming economy needed no stimulus. That was in part to provide liquidity to a Y2K-wary public and partly in response to the 1998 market turmoil, but they were slow to withdraw the extra cash. Bernanke was again generous to borrowers in the 2000s, contributing to the housing crisis and Great Recession. We’re now 20 years into training people (and businesses) that running up debt is fun and easy… and they’ve responded.
But over time, debt stops stimulating growth. Over this series, we will see that it takes more debt accumulation for every point of GDP growth, both in the US and elsewhere. Hence, the flat-to-mild “recovery” years. I’ve cited academic literature via my friend Lacy Hunt that debt eventually becomes a drag on growth.
Debt-fueled growth is fun at first but simply pulls forward future spending, which we then miss. Now we’re entering the much more dangerous reversal phase in which the Fed tries to break the debt addiction. We all know that never ends well.
So, Peter’s point is that a Fed-driven credit cycle now supersedes the traditional business cycle. Since debt drives so much GDP growth, its cost (i.e. interest rates) is the main variable defining where we are in the cycle. The Fed controls that cost—or at least tries to—so we all obsess on Fed policy. And rightly so.
Among other effects, debt boosts asset prices. That’s why stocks and real estate have performed so well. But with rates now rising and the Fed unloading assets, those same prices are highly vulnerable. An asset’s value is what someone will pay for it. If financing costs rise and buyers lack cash, the asset price must fall. And fall it will. The consensus at my New York dinner was recession in the last half of 2019. Peter expects it sooner, in Q1 2019.
If that’s right, financial market fireworks aren’t far away.
Corporate Debt Disaster
In an old-style economic cycle, recessions triggered bear markets. Economic contraction slowed consumer spending, corporate earnings fell, and stock prices dropped. That’s not how it works when the credit cycle is in control. Lower asset prices aren’t the result of a recession. They cause the recession. That’s because access to credit drives consumer spending and business investment. Take it away and they decline. Recession follows.
If some of this sounds like the Hyman Minsky financial instability hypothesis I’ve described before, you’re exactly right. Minsky said exuberant firms take on too much debt, which paralyzes them, and then bad things start happening. I think we’re approaching that point.
The last “Minsky Moment” came from subprime mortgages and associated derivatives. Those are getting problematic again, but I think today’s bigger risk is the sheer amount of corporate debt, especially high-yield bonds that will be very hard to liquidate in a crisis.
Corporate debt is now at a level that has not ended well in past cycles. Here’s a chart from Dave Rosenberg:
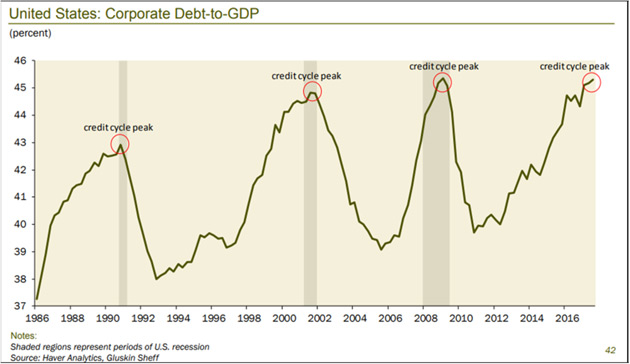
Source: Gluskin Sheff
The Debt/GDP ratio could go higher still, but I think not much more. Whenever it falls, lenders (including bond fund and ETF investors) will want to sell. Then comes the hard part: to whom?
You see, it’s not just borrowers who’ve become accustomed to easy credit. Many lenders assume they can exit at a moment’s notice. One reason for the Great Recession was so many borrowers had sold short-term commercial paper to buy long-term assets. Things got worse when they couldn’t roll over the debt and some are now doing exactly the same thing again, except in much riskier high-yield debt. We have two related problems here.
- Corporate debt and especially high-yield debt issuance has exploded since 2009.
- Tighter regulations discouraged banks from making markets in corporate and HY debt.
Both are problems but the second is worse. Experts tell me that Dodd-Frank requirements have reduced major bank market-making abilities by around 90%. For now, bond market liquidity is fine because hedge funds and other non-bank lenders have filled the gap. The problem is they are not true market makers. Nothing requires them to hold inventory or buy when you want to sell. That means all the bids can “magically” disappear just when you need them most. These “shadow banks” are not in the business of protecting your assets. They are worried about their own profits and those of their clients.
Gavekal’s Louis Gave wrote a fascinating article on this last week titled, “The Illusion of Liquidity and Its Consequences.” He pulled the numbers on corporate bond ETFs and compared it to the inventory trading desks were holding—a rough measure of liquidity.
Louis found dealer inventory is not remotely enough to accommodate the selling he expects as higher rates bite more.
We now have a corporate bond market that has roughly doubled in size while the willingness and ability of bond dealers to provide liquidity into a stressed market has fallen by more than -80%. At the same time, this market has a brand-new class of investors, who are likely to expect daily liquidity if and when market behavior turns sour. At the very least, it is clear that this is a very different corporate bond market and history-based financial models will most likely be found wanting.
The “new class” of investors he mentions are corporate bond ETF and mutual fund shareholders. These funds have exploded in size (high yield alone is now around $2 trillion) and their design presumes a market with ample liquidity. We barely have such a market right now, and we certainly won’t have one after rates jump another 50–100 basis points.
Worse, I don’t have enough exclamation points to describe the disaster when high-yield funds, often purchased by mom-and-pop investors in a reach for yield, all try to sell at once, and the funds sell anything they can at fire-sale prices to meet redemptions.
In a bear market you sell what you can, not what you want to. We will look at what happens to high-yield funds in bear markets in a later letter. The picture is not pretty.
To make matters worse, many of these lenders are far more leveraged this time. They bought their corporate bonds with borrowed money, confident that low interest rates and defaults would keep risks manageable. In fact, according to S&P Global Market Watch, 77% of corporate bonds that are leveraged are what’s known as “covenant-lite.” We’ll discuss more later in this series, but the short answer is that the borrower doesn’t have to repay by conventional means. Sometimes they can even force the lender to take more debt. In an odd way, some of these “covenant-lite” borrowers can actually “print their own money.”
Somehow, lenders thought it was a good idea to buy those bonds. Maybe that made sense in good times. In bad times? It can precipitate a crisis. As the economy enters recession, many companies will lose their ability to service debt, especially now that the Fed is making it more expensive to roll over—as multiple trillions of dollars will need to do in the next few years. Normally this would be the borrowers’ problem, but covenant-lite lenders took it on themselves.
The macroeconomic effects will spread even more widely. Companies that can’t service their debt have little choice but to shrink. They will do it via layoffs, reducing inventory and investment, or selling assets. All those reduce growth and, if widespread enough, lead to recession.
Let’s look at this data and troubling chart from Bloomberg:
Companies will need to refinance an estimated $4 trillion of bonds over the next five years, about two-thirds of all their outstanding debt, according to Wells Fargo Securities. This has investors concerned because rising rates means it will cost more to pay for unprecedented amounts of borrowing, which could push balance sheets toward a tipping point. And on top of that, many see the economy slowing down at the same time the rollovers are peaking.
“If more of your cash flow is spent into servicing your debt and not trying to grow your company, that could, over time—if enough companies are doing that—lead to economic contraction,” said Zachary Chavis, a portfolio manager at Sage Advisory Services Ltd. in Austin, Texas. “A lot of people are worried that could happen in the next two years.”
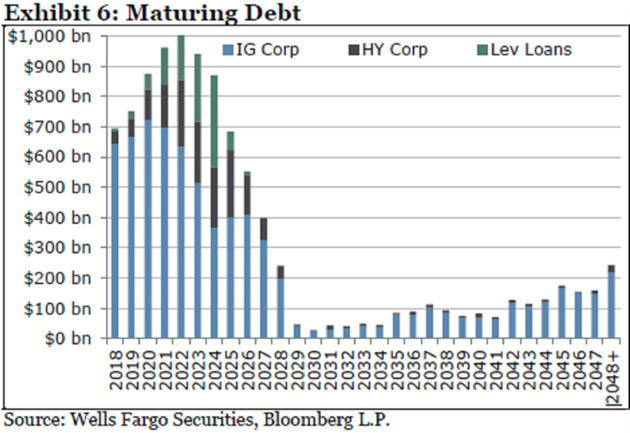
The problem is that much of the $2 trillion in bond ETF and mutual funds isn’t owned by long-term investors who hold maturity. When the herd of investors calls up to redeem, there will be no bids for their “bad” bonds. But they’re required to pay redemptions, so they’ll have to sell their “good” bonds. Remaining investors will be stuck with an increasingly poor-quality portfolio, which will drop even faster. Wash, rinse, repeat. Those of us with a little gray hair have seen this before, but I think the coming one is potentially biblical in proportion.

Casey Jones via Wikimedia Commons
Blowing the Whistle
As you can tell, this is a multifaceted problem. I will dig deeper into the specifics in the coming weeks. The numbers seem unbelievable. I truly think we are headed to a staggering credit crisis.
I began this letter describing the coming events as a train wreck. That comparison came up when my colleague Patrick Watson and I were on the phone this week, planning this series of letters. Patrick and his beautiful wife Grace had just come back from Tennessee, and he told me about visiting the Casey Jones birthplace museum in Jackson.
For those who don’t know the story or haven’t heard the songs, Casey Jones was a talented young railroad engineer in the late 1800s. On April 30, 1900, Casey Jones was going at top speed when his train tragically overtook a stopped train that wasn’t supposed to be there.
Traveling at 75 miles per hour, Jones ordered his young fireman to jump, pulled the brakes hard, and blew the train whistle, warning his passengers and the other train. Later investigations found he had slowed it to 35 mph before impact. Everyone on both trains survived… except Casey Jones.
His heroic death made Jones a folk hero to this day. Many songs told the story and even the Grateful Dead and AC/DC paid tribute decades later. (Trivia: He actually tuned his train whistle with six different tubes to make a unique whippoorwill sound. So, when people heard his train whistle, they knew it was Casey Jones.)
Right now, the US economy is kind of like that train: speeding ahead with the Fed only slowly removing the fuel it shouldn’t have loaded in the first place and passengers just hoping to reach our destination on time. Unfortunately, we don’t have a reliable Casey Jones at the throttle. We’re at the mercy of central bankers and politicians who aren’t looking ahead. They can’t simply turn the steering wheel. We are stuck on this track and will go where it takes us.
Next week, we’ll talk about the sequence of how the next debt crisis will arise, how it triggers a recession, and then $2 trillion of deficits in the US and rising debt all over the world. Which just increases pressures on interest rates and lending. And reduces growth. It is not a virtuous cycle.
My Writing Productivity Secret
About ten years ago, I began experimenting with voice recognition technology. For the first few years the software just wasn’t “ready.” Then about four years ago, Nuance came out with a greatly improved version which has since gotten even better. The new Dragon Professional 15 is amazingly flexible with top-of-the-line recognition accuracy.
Frankly, Dragon voice recognition technology by Nuance makes me at least three times more productive in my writing. Now, even though I have written millions of words, I am still not all that fast a typist. Dragon has changed that.
I don’t often endorse products, but I am so thoroughly satisfied with Dragon that I am comfortable this time. I arranged for Nuance to offer an exclusive 50% discount to my readers that you can access here. If you are a serious writer or simply prefer to answer emails by voice, this is an amazing productivity tool. And it can do so many other things as well. Click here to learn more.
After a few minutes of training your own personal Dragon to recognize your unique speaking voice—and becoming familiar with the, well, nuances—I think you will be as happy as I am. After all, who doesn’t want to save time and breeze through your writing three times faster? Try it.
Chicago, Orange County, and Raleigh
My next trip will be to a private conference in Chicago for my friends Swan Global Investments. I’ll also meet with old friend Raghuram Rajan, former Reserve Bank of India head and now on the Chicago Booth faculty. Then I fly to Orange County to speak at the CFA Society on May 17. The next week I go to Raleigh, North Carolina, to see old friends and speak at The Investment Institute. Then at some point in June, I’ll be in Cleveland for an overdue medical checkup with Dr. Mike Roizen.
On a personal note, the transition to the new and improved Over My Shoulder has taken me back almost 30 years to when I first hired Patrick Watson as a full-time research assistant. He has been with me through several companies and has worked in others, but now he’s back with me full time. It is very rewarding to have such a long-lasting relationship. He’s probably read more of my writing than anyone I know. Along with a few other changes in my business and personal life, my productivity is already increasing noticeably. I’m very excited about the ways Patrick and I can help enhance your life as well.
This week, Pat Caddell was in town for a meeting and came to stay at my home yesterday and share anecdotes. We really hit it off at my conference, and we’re having some fascinating discussions. He is a very interesting, old-school gentleman.
It’s time to hit the send button. Somewhere in my travels, I picked up a nasty chest cold that my doctor says will take me about a week to recover from, if I’m lucky. Thankfully it is already improving, but I’ve been taking more medicine and cough drops than I like. This too shall pass, though. Have a great week.
Your thinking a lot about credit cycles analyst,
 While the majority keep bashing the Federal Reserve, other central banks seem to escape any criticism. The European Central Bank under Mario Draghi has engaged in what history will call the Great Monetary Experiment of the 21st Century – the daring experiment of negative interest rates. A look behind the scenes reveals that this experiment has been not just a failure, it has undermined the entire global economic structure. We are looking at pension funds being driven into insolvency as the traditional asset allocation model of 60% equity 40% bonds has failed to secure the future with negative interest rates. Then, the ECB has exceeded 40% ownership of Eurozone government debt. The ECB realizes it can not only sell any of its holdings ever again, it cannot even refuse to reinvest what it has already bought when those bonds expire. The Fed has announced it will not reinvest anything. Draghi is trapped. He cannot stop buying government debt for if he does, interest rates will soar. He cannot escape this crisis and it is not going to end nicely.
While the majority keep bashing the Federal Reserve, other central banks seem to escape any criticism. The European Central Bank under Mario Draghi has engaged in what history will call the Great Monetary Experiment of the 21st Century – the daring experiment of negative interest rates. A look behind the scenes reveals that this experiment has been not just a failure, it has undermined the entire global economic structure. We are looking at pension funds being driven into insolvency as the traditional asset allocation model of 60% equity 40% bonds has failed to secure the future with negative interest rates. Then, the ECB has exceeded 40% ownership of Eurozone government debt. The ECB realizes it can not only sell any of its holdings ever again, it cannot even refuse to reinvest what it has already bought when those bonds expire. The Fed has announced it will not reinvest anything. Draghi is trapped. He cannot stop buying government debt for if he does, interest rates will soar. He cannot escape this crisis and it is not going to end nicely.
When this policy collapses, forced by the free markets (no bid), CONFIDENCE will collapse rapidly. Once people no longer believe the central banks can control anything, the end has arrived. We will be looking at the time at the WEC (Singapore – June 15-16, 2018 Orlando – November 16-17, 2018). We will be answering the question – Can a central bank actually fail?
….also from Martin: Market Talk- April 17, 2018
and:
The Sovereign Debt Crisis has Spread to 119 Countries (The Sovereign Debt Crisis is on schedule to be noticed starting here in 2018)
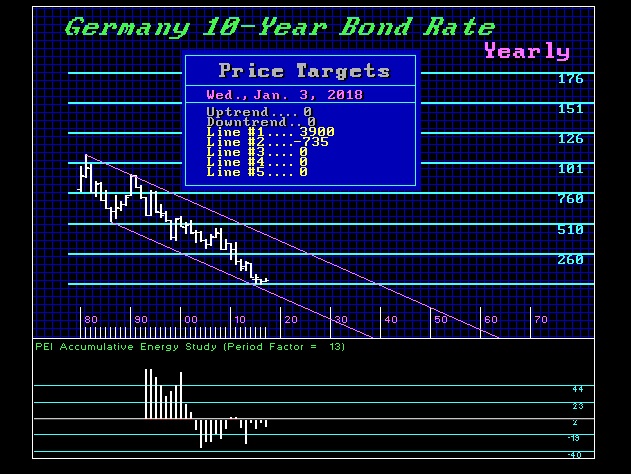
Martin Armstrong reports the latest movements on the interest rate front as well as the remarkable move by Germany which will convince the world the European project is authoritarian (Germany arrested a Catalonian politician enforcing Spain’s dictatorship) – R. Zurrer for Money Talks
QUESTION: Mr. Armstrong; It appears that now the Bundesbank has adopted your view of rising interest rates. How fast do you see rates rising?
ANSWER: Yes, the Bundesbank President Jens Weidmann has come out and warned that banks should start to make provisions for interest rate risks associated with rising interest rates. The normalization of the interest rates is essential and as always, it is now too little too late. The economic environment is changing much more rapidly than most suspect. It is true that the German banks have increased their equity significantly since the financial crisis. While the central banks are warning that rates are rising, they misjudge the fact that banks are by no means as resilient as they were before the 2007-2009 crisis.
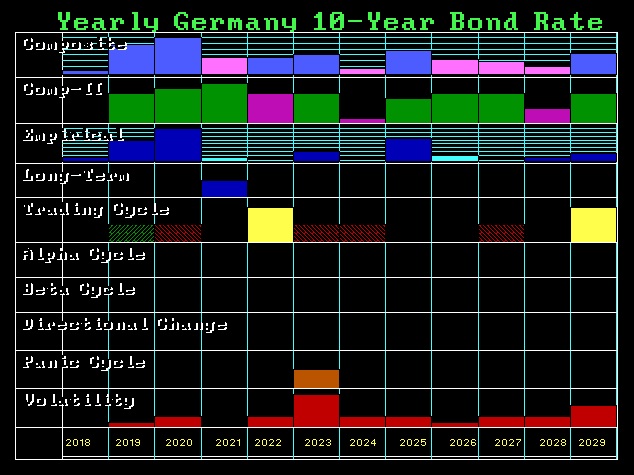
German 10-year rates will start to rise rapidly following a monthly closing above 0.79%. The next stop will be 2% and thereafter, we will see a test of the 4% level. Once we exceed the 2007 high of 4.67%, we will see a rapid rise to the 5.6% area and an annual closing above that will warn of a test of the 8.5%-11% zone and that can be easily by 2020.
….related from Martin: The Fed is Raising Rates Because of the Pension Crisis
…also breaking: Germany Arrests Former Head of Catalonia for Spain Confirm the Spanish Constitution Violates Human Rights
Right now, most analysts think higher interest rates are on the way. Given the majority is always wrong when it comes to markets, Martin makes two predictions on how that will play into the expectations for higher interest rates. – R. Zurrer for Money Talks

MARTIN’S ANSWER: With the Federal Reserve stating they must “normalize” interest rates since 2014, of course, the majority will view that will be the trend. We are at a 5,000 low in rates historically. Naturally, the only direction is now UP, UP, and AWAY! There are two ways that they will be wrong and that has to do with their interpretation.
First, they will not comprehend just HOW fast rates will rise or WHY!
Second, they will interpret higher rates as BEARISH for equities, as they traditionally do.
Therefore, the way the MAJORITY will be wrong is not in the mere fact that rates will rise, they read the statement of the central banks. It is the interpretation of what will follow from the simple trend. In equities, every new high was to be the last from 2009 right up to 2018.
….also an update on Martin’s “Interbank Rates Starting to Rise – Monetary Crisis is Beginning“:
Eurozone Banking Crisis – ECB Delays Rules for Bad Loans until 2021
…more trouble for Europe: Will US Companies Repatriating Cash Home Create Banking Crisis Outside USA?