Investment/Finances
The American economy could experience painfully slow growth and stubbornly high unemployment for a decade or longer as a result of the 2007 collapse of the housing market and the economic turmoil that followed, according to an authority on the history of financial crises.
That finding, contained in a new paper by Carmen M. Reinhart, an economist at the University of Maryland, generated considerable debate during an annual policy symposium here, organized by the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City, which concluded on Saturday.
Watching economists and media analysts react to breaking economic news is a bit like looking at a flock of pigeons flying over the New York skyline. A true wonder of the urban landscape, the flocks can include hundreds of individuals who show an uncanny ability to stay in tight formation as the group quickly zig-zags between buildings. What may be even more remarkable than their ability to randomly fly while maintaining cohesion is the flock’s refusal to stick to any particular direction for very long, and their determination to fly feverishly without actually going anywhere. Sound familiar?
The latest weak United States gross domestic product data numbers have finally…..
…..read more HERE
Growing up a century ago in sunny Calabria, on the shore of the Tyrrhenian Sea, my grandfather would never have dreamed that the common shrimp and calamari he had to eat every day would ever be considered a luxur y; but for his grandson, growing up in Chicagoland sixty years later, a thousand miles from any coast, they certainly were. A luxury, a rare treat.
These little extravagances — not the major ones like Rolls-Royces and Ferraris — are important to one’s enjoyment of life, and they represent, as much as anything else, the great opportunities of America. For here, even the broke, even the unemployed can indulge in a little luxury now and then. It can help us get through the day, help us endure life’s little problems.
For one, it’s the appetizer of fried calamari before the meal; for another, it’s the dessert afterward. For one, it’s splurging on a collectible to display in an étagère; for another, it’s the solid brass door handle to install on the front door. Some might call one a waste of money; others might ask why something they think a necessity is on this list at all.
No matter; in a free country, we each have the right to our little extravagances. Perhaps that’s one aspect of what the Founders meant by “the pursuit of happiness”: our government was to be one that would let its citizens enjoy their lives, in their own way, without standing athwart such little personal desires.
…Unless, that is, your personal little extravagance happens to be a soothing shower at the end of the day — using a showerhead that consumes more than 2.5 gallons of water per minute. Then the modern American nanny state steps in and declares, “You’re wasting water, you sinner! Cease and desist!”
In 1992, the Department of Energy managed to promulgate a regulation requiring that showerheads use no more than 2.5 gallons per minute as an effort to save…water. This is a substance that’s in such short supply that 75% of the planet is covered with it.
Now there are certainly areas of the world, even of America, with chronic or frequent water shortages — California and Arizona, the inland deserts, the areas where government-run or government-managed utilities have failed to provide their residents with access to one of the most plentiful substances on earth. These specific areas can easily deal with such issues by passing ordinances requiring usage meters or timers or perhaps even banning the use of high-flow showerheads, where and when appropriate to do so.
But a federal limit, equally applicable nationwide, even in areas where there has never been, and never will be, such a shortage? What on earth for?
For eighteen years, this regulation was interpreted one way — the limitation was per nozzle, so people desiring a more vigorous shower could simply install a couple more showerheads, or a multi-nozzle shower system. A specialty arose in the marketplace: the creative design of elegant and invigorating shower systems.
These systems are for the rich who want to be self-indulgent, for the business traveler or vacationer seeking a more exhilarating shower at his hotel, sure, but they’re also for the working man who comes home caked in factory grime; for the plumber, carpenter, or electrician who spent his day between hot walls or floors of buildings under construction; for the roofer or window installer whose day was spent on scaffolding, sweating under the hot sun.
Who are we to judge them if they want to spend another hundred bucks on a fancier showerhead than the standard nozzle, plus another buck or two a month on the water bill? If they deem it worthwhile for themselves, and are willing to pay for it, who are we to say no, in a land in which the pursuit of happiness is an inalienable right?
In May 2010, the Department of Energy clarified their interpretation of the rule: it’s 2.5 gallons, period. Not per nozzle, but per entire system. And they made it as clear as they could in the language of lawyers: by suing manufacturers who had dared defy the powers that be by obeying the interpretation that had held sway for eighteen years, instead of anticipating the interpretation that the Obama administration would suddenly decide upon.
In a heartbeat, every manufacturer, distributor, seller, and installer of high-flow showerheads across the country had to stop and check their product lines, shutting down assembly lines in factories, taking products off the shelves, putting a hold on construction and remodeling projects while plans were studied, while alternatives were sought, while substitutions were evaluated and selected.
As outrageous as this may be, at least it can serve for us as a microcosm of the dangers of the nanny state and of the utterly counterproductive nature of the Obama administration’s idea of its role in the economy.
It’s a new twist on the famed Broken Window Fallacy in economics. By banning one product — essentially destroying the product’s value in commerce at the stroke of a pen — the government forces the manufacturing and installation communities to develop and manufacture a replacement that meets the new code. It would appear at first blush to create new jobs. Unfortunately, here in the real world, such a solution is infinitely worse than the alleged problem (wasting a little water) could ever have been. Consider:
In days of old, when a company decided to explore a redesign of their product, it would usually do so within its own country. Its own engineers on the third floor would study the blueprints, looking for opportunities for quality improvement, cost-savings, or style updates. Its purchasing department, on the second floor, would bid out raw materials, intermediate parts, and other components to other nearby vendors, again seeking cost savings without sacrificing the quality of the tried and true. Back by the shipping dock, the traffic department would negotiate a trucking rate so that the new vendor could ship the cargo for the same cost or less as the old vendor.
Saving money and improving the finished product this way, by finding a new supplier for this gasket or that valve, for this piping or that brass casting, is what keeps our productivity measurements ticking up every month. America is the king of such productivity improvements.
In any case, in the old days, they would still make the finished product in their own factory, albeit with a few different parts, with no other possibility crossing their minds. A Detroit automaker was and would remain a Detroit automaker; a Chicago television maker or Camden phonograph maker was just that and would never change.
No longer. Manufacturers and distributors engage in international trade without a second thought, so just as we have flung open the doors to exports, we have simultaneously flung open the doors to the possibility of importing as well. Such globalization is a wonderful process, without question. It has provided the world with greater access to the blessings of capitalism, freeing millions from their nations’ formerly inescapable poverty, welcoming them into the unlimited potential of the free market.
But globalization can have its downside. Just as it broadens our sales possibilities, opening up new customers in new markets, it gives us new vendors to choose from, breaking down the walls of protection that once existed, so we are no longer shielded from the natural effects of our own destructive policies.
If the USA has a 38% effective business tax rate, when Ireland’s is a mere 11%, might Ireland, enjoying such a lower tax burden, be able to offer just as good a gasket for a lower price?
If the USA has skyrocketing property taxes on factories, because politicians learned somewhere along the way that homeowners vote and businesses don’t, might a country without the same burden of property taxes provide a temptingly competitive alternative vendor for that valve?
If the USA has such an infestation of plaintiffs’ attorneys that our businesses have to employ an army of their own defense attorneys to fend them off, and fund costly liability insurance policies just in case, mightn’t a country without such flaws be able to offer the same quality brass casting for a lower price?
Today, we outsource the materials, the intermediate components, the castings — even the engineering, the R&D, the printing of brochures. As our government makes domestic functions and production ever more unnecessarily painful, our manufacturing community survives as it must: by outsourcing.
Worse still, once we outsource, we rarely go through the trouble of insourcing again. If at this moment in time it is cheaper to buy the casting from China, then even if that cost-benefit analysis should change in a year or two, it’s rare that the buyer will switch back. Every vendor change has a cost; it’s not done unless forced by the bottom line or by upper management. So at a time when outsourcing abroad is perhaps more tempting than usual — more tempting than (hopefully) it will be a year or two hence — this is no time to be pushing companies to open up more and more products to such potentially irrevocable sourcing reviews!
We are watching our industries exit our shores at a breakneck clip, as other countries welcome them in with taxation less burdensome, and an atmosphere less hostile, than our own. The United States, the engine of manufacturing innovation and capitalist growth for centuries, has ground to a halt.
Many businesses — and their product lines — can survive on reputation, quality, and sheer inertia for years, long enough perhaps to wait out the current crisis, ready to enjoy the boom that will surely result when current policies are reversed and America becomes business-friendly again. If only we don’t make it worse unnecessarily; if only we don’t kick them all while they’re down.
But that’s what this administration is doing, day after day, in industry after industry. Car salesmen and technicians had a slow year in 2009 until their own president ordered some three thousand dealers shut down completely. The roughnecks in the Gulf of Mexico were hard at work on oil rigs until their own president capriciously banned offshore drilling this summer. Those multi-nozzle showerhead makers were sputtering along through the recession until their own Department of Energy turned off the water completely.
In the quest for improved productivity, American manufacturers will always bid out their parts, their engineering, and their finished products. It’s why they succeed in the first place. But this is no time to push them even harder, no time to keep reminding every purchasing agent, every engineer, every investor, of that thought lurking in the back of their minds: “You know, it really would be cheaper to just close up completely and move offshore.”
It’s not too late; we can fix this mess. A couple of years of responsible policies can undo most of the recent damage. But to grow a stronger manufacturing sector, we have to have something to work with. We’ll be able to grow it only if it hasn’t been killed outright before we get our chance.
John F. Di Leo is an international trade compliance trainer based in Chicago. His columns regularly appear in Illinois Review. This one appeared in American Thinker
As wishy-washy as it gets, but in the end, hope won out over despair. The speech by Fed Chairman Bernanke was all over the map and was noncommittal in terms of offering an iron clad forecast despite the title being The Economic Outlook and Monetary Policy. The sermon was littered with caveats in the form of “should”, “despite”, “although”, “possibly”, and “however” — but in the end, he expressed optimism (then again, what else can he do in public?). He obviously learned his lesson from using words such as “unusually uncertain”, which he used to describe the economic outlook at his recent Congressional testimony in July when the Dow responded by diving 109 points (as if things haven’t become even more uncertain since, but why tell anyone?).
Here are some of the snippets from the speech — Mr. Bernanke seems to have a different crystal ball than we do, as he is optimistic that growth will be sustained in the second half of this year and improve next year. At the same time, he acknowledges that the economy has not improved as much as the Fed was forecasting earlier (that is old news). But what really stood out in his speech was the extent to which it was so “on the one hand, but then on the other hand”, which of course is why economists are constantly ridiculed.
On the one hand …
• “For a sustained expansion to take hold, growth in private final demand — notably, consumer spending and business fixed investment — must ultimately take the lead. On the whole, in the United States, that critical handoff appears to be under way.”
• “Expansionary fiscal policies and a powerful inventory cycle, helped by a recovery in international trade and improved financial conditions, fueled a significant pickup in growth.”
• “Stronger balance sheets should in turn allow households to increase their spending more rapidly as credit conditions ease and the overall economy improves.”
• “I expect the economy to continue to expand in the second half of this year, albeit at a relatively modest pace.”
• “Despite this recent slowing, however, it is reasonable to expect some pickup in growth in 2011 and in subsequent years.” [Ed note: the markets picked up on this].
• “Despite the weaker data seen recently, the preconditions for a pickup in growth in 2011 appear to remain in place.”
• “Consumers are reducing their debt and building savings, returning household wealth-to-income ratios near to longer-term historical norms. Stronger household finances, rising incomes, and some easing of credit conditions will provide the basis for more-rapid growth in household spending next year.”
… But on the other hand
• “However, although private final demand, output, and employment have indeed been growing for more than a year, the pace of that growth recently appears somewhat less vigorous than we expected.”
• “Notwithstanding some important steps forward, however, as we return once again to Jackson Hole, I think we would all agree that, for much of the world, the task of economic recovery and repair remains far from complete.”
• “At best, though, fiscal impetus and the inventory cycle can drive recovery only temporarily.”
• “Incoming data on the labor market have remained disappointing. Private- sector employment has grown only sluggishly, the small decline in the unemployment rate is attributable more to reduced labor force participation than to job creation, and initial claims for unemployment insurance remain high. Firms are reluctant to add permanent employees, citing slow growth of sales and elevated economic and regulatory uncertainty. In lieu of adding permanent workers, some firms have increased labor input by increasing workweeks, offering full-time work to part-time workers, and making extensive use of temporary workers.”
• “The prospect of high unemployment for a long period of time remains a central concern of policy. Not only does high unemployment, particularly long- term unemployment, impose heavy costs on the unemployed and their families and on society, but it also poses risks to the sustainability of the recovery itself through its effects on households’ incomes and confidence.”
• “Although what I have just described is, I believe, the most plausible outcome, macroeconomic projections are inherently uncertain, and the economy remains vulnerable to unexpected developments.” [Ed note: the market did not pick up on this]. In the final analysis, if there was a commitment made, it is that Mr. Bernanke will use all of his power to ensure that the recovery will remain intact:
“The Committee will certainly use its tools as needed to maintain price stability– avoiding excessive inflation or further disinflation–and to promote the continuation of the economic recovery …. the Federal Reserve remains committed to playing its part to help the U.S. economy return to sustained, noninflationary growth.”
What is interesting is the choice of the word “return” to “sustained” growth, which implies that despite his high hopes for the future, this is a state (the word “return” by definition means “revert to a previous state”) we have to achieve (sustainable growth) which is remarkable when one considers all the radical efforts that the central bank and the government have made to bolster the economy. As we are finding out, even with an extremely aggressive central bank, just because you turn the key doesn’t mean the engine turns over.
Also in Lunch with Dave:
• Revisionists unite! Economists are now in the process of cutting their GDP forecast for the U.S.
• U.S. real GDP better than expected, but …
• Consumer sentiment, as per the University of Michigan index, came in a tad below expected in August, at 69.6
• Market commentary: Dow below the 10k mark and the S&P is trading close to that 1,040 line; bonds hitting some major resistance, but the trend in yields are still clearly down
• Deflationary expectations: consumers in the U.S. are holding off to buy back-to-school items in hopes of lower prices to come
• The bear market in housing starts is still far from over
• Initial jobless claims improve but it could be a headfake due to seasonals; keep it simple, claims are at recessionary levels
• Kansas yes, Royal no: the KC Fed index collapsed in August
• You call this good news? Mortgage delinquency dipped to 9.85% from 10.06% a year ago
• What is a depression anyway?
…..subscribe to David Rosenbergs Economic Reports HERE
From BHP Billiton’s mid-year presentation, here are the three reasons they’re concerned about what the future holds.
First, austerity
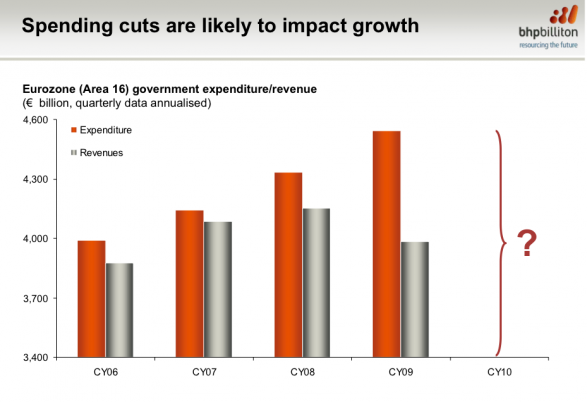
Second, debt levels.

And third, China.
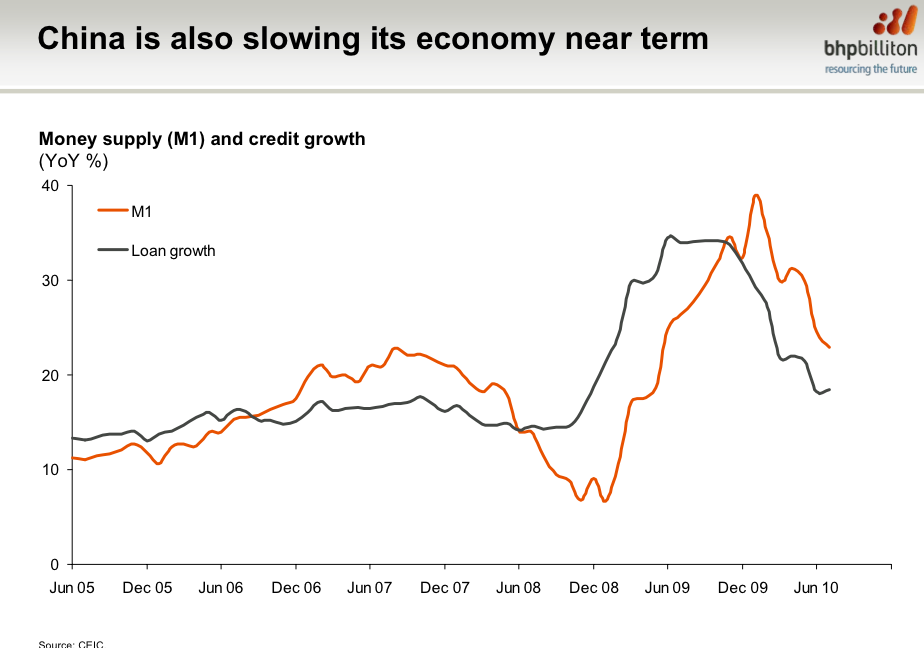
BHP Sounds The Alarm On Global Growth And Commodity Prices
How does the world’s biggest miner, and the possible acquire of Potash for $39 billion, see the global outlook?
They’re pretty nervous. The following comments come from the company’s mid-year report.
….read it all HERE
YOU CALL THIS CAPITULATION?
by David Rosenberg
Short interest on the Nasdaq down 1.6% in the first week of August? The Rasmussen investor confidence index at 80.4? Call us when it hits 50, which in the past was a “classic” washout level.
Investors Intelligence did show the bull share declining further this past week, to 33.3% from 36.7%. But the bear share barely budged and is still lower than the bull share at 31.2%. Are we supposed to believe that at the market lows, there will still be more bulls than bears out there? Hardly. At true lows, the bulls are hiding under table screaming “uncle!”.
Yes, Market Vane equity sentiment is down to 46, but in truth, this metric is usually in a 20-30% range when the market correction ends. We are waiting patiently.
As for bonds, well, Market Vane sentiment is 73%. Now what is so bubbly about that. Call us on extreme positive sentiment when this measure of excessive bullishness is closer to 90%, and we’ll be in the correction camp hopefully by the time this happens.
In any event, the extent of the denial over U.S. double-dip risks is unbelievable. These are quotes from economists and strategists in yesterday’s print media — and just a select list at that for there was just so much surreal commentary: “I’d be shocked if you don’t make a lot money in U.S. stocks over the next decade.”
“If yields rise, then 30-year bonds will suffer.”
“It won’t be a double-dip recession but it might feel like it.” “There is a global perception that we are not necessarily going into a Japan-type scenario, there is a recognition of a slow recovery.” “People shouldn’t panic.”
At market lows, the recession rhetoric becomes more intense and indeed it’s when people do panic that the best buying opportunities generally occur.










