
IN EARLY October the IMF looked at what might happen to the world economy if conflict in Iraq caused an oil-price shock. Fighters from Islamic State (IS) were pushing into the country’s north and the fund worried about a sharp price rise, of 20% in a year. Global GDP would fall by 0.5-1.5%, it concluded. Equity prices in rich countries would decline by 3-7%, and inflation would be at least half a point higher.
IS is still advancing. Russia, the world’s third-biggest producer, is embroiled in Ukraine. Iraq, Syria, Nigeria and Libya, oil producers all, are in turmoil. But the price of Brent crude fell over 25% from $115 a barrel in mid-June to under $85 in mid-October, before recovering a little (see chart). Such a shift has global consequences. Who are the winners and losers?
The first winner is the world economy itself. A 10% change in the oil price is associated with around a 0.2% change in global GDP, says Tom Helbling of the IMF. A price fall normally boosts GDP by shifting resources from producers to consumers, who are more likely to spend their gains than wealthy sheikhdoms. If increased supply is the driving force, the effect is likely to be bigger—as in America, where shale gas drove prices down relative to Europe and, says the IMF, boosted manufactured exports by 6% compared with the rest of the world. But if it reflects weak demand, consumers may save the windfall.
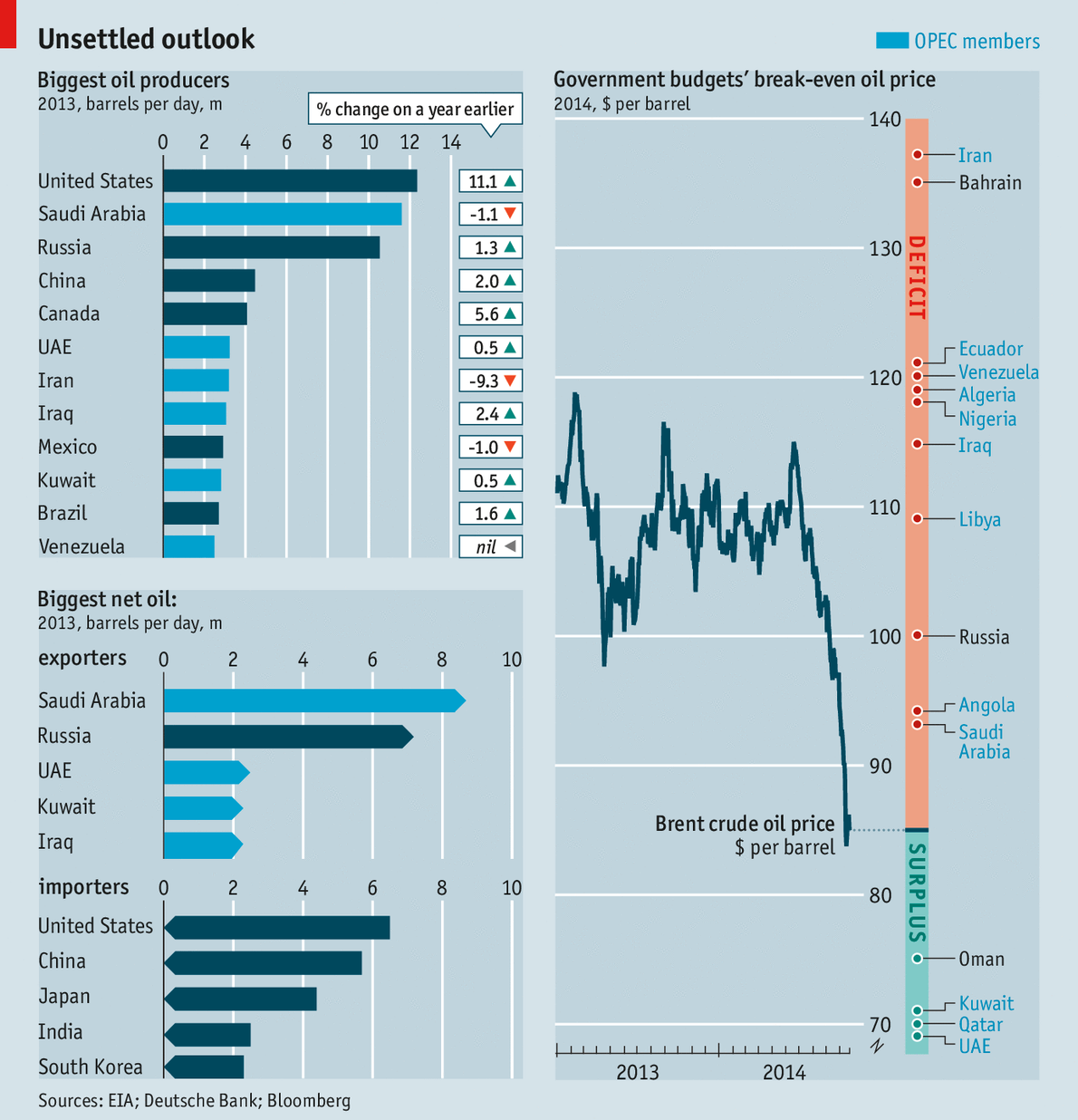
Today’s falling prices are caused by shifts in both supply and demand. The world’s slowing economy, and….
….continue reading HERE












