For more insights from Sprott Global Resource Investments, sign up for the free Sprott’s Thoughts newsletter.
Securities Disclosure: I, Vivien Diniz, hold no investment interest in any of the companies mentioned.
Related reading:
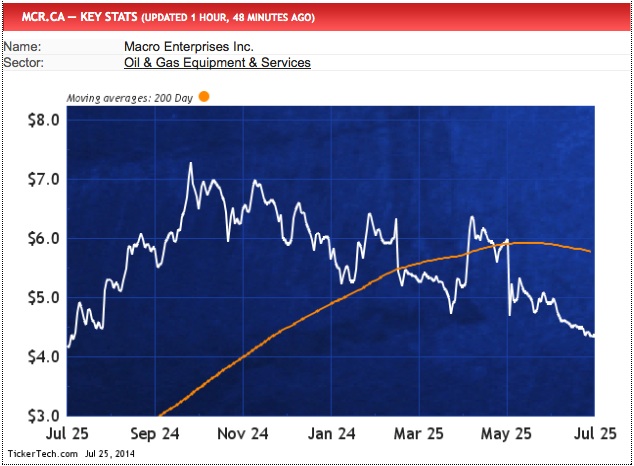
Read full article in a new window: RSI Alert: Macro Enterprises (CVE:MCR.CA) Now Oversold
Once upon a time, there were safe havens in this world, places where investors could hide when the going got rough. If you believe this fairy tale world will persist, pinch yourself. In our assessment, not only are there no safe havens left, but instability may be the new normal. Is your portfolio ready?

In a ‘typical’ crisis, if there is such a thing:
• First, the equity markets tend to have a broad sell-off as risky assets become less popular. Historically, this is where the U.S. dollar or cash in general has been king. In the Eurozone debt crisis, in this phase, the Euro was sold as a proxy for all things bad in the Eurozone.
• As a crisis evolves, markets tend to become more differentiating. When Cyprus “blew up,” Spain had a Treasury auction paying the lowest yields since the early 1990s.
• Moving on even further, the markets get used to the crisis. When a Portuguese company didn’t pay its loans on time, the markets barely blinked. Part of it was that the risk seemed manageable; but part of it was also that even though crisis management in the Eurozone continues to be far from perfect, participants kind of know the game plan to expect. With that, risk can be priced more appropriately.
Based on this pattern, pundits are quick to encourage investors not to sell and to buy the dips as the recovery is all but assured. Except, of course, if you had your money in Cyprus. The ‘buying the dip’ mentality has reached extremes; arguably, for good reason: by promising to keep rates lower for longer, the Federal Reserve and other central banks around the world have compressed risk premia. That is, the premium demanded for “risky” assets has come down. This may be most apparent in the low yields in junk bonds, an area Fed Chair Janet Yellen has called bubbly, even if her very policies are a key driver. In Europe, European Central Bank (ECB) Chief Mario Draghi has promised to do ‘whatever it takes.’ So why shouldn’t investors chase yields in the weaker Eurozone countries?
What could possibly go wrong?
Anything that looks too good to be true usually is. When risk premia is artificially depressed, it is understandable that volatility is also depressed. But if risk premia expands once again, for whatever reason, asset prices may be at risk. That’s because investors may be less inclined to buy stocks or junk bonds if it suddenly deems riskier. It can be as little as perception (“the glass is suddenly half empty”); it can be the Fed trying to engineer an ‘exit;’ or, for example, it can be geopolitical uncertainty.
There will be lots of confusing signals. For example, for a bit over a year now, the euro appeared to be the preferred “safe haven” – as investors fled emerging bond markets, it didn’t make it to the U.S. dollar, but to places such as Spanish and Portuguese bonds. Of late, though, the dollar appears to show baby steps of yet again being preferred over the euro. But don’t be fooled: the euro is weaker because of the risk that Russia might turn off the gas supply to Europe if the Ukrainian crisis were to escalate. Yet again, while the dollar has strengthened a tiny bit, the yield chasers mostly went right back into emerging markets, with some currencies there rising versus the greenback. This appears more a shuffle by high stakes yield chasers rather than a flight to safety.
While anyone may be excused for being confused by the headlines, consider the medium term outlook: pundits have suggested the Fed will only engineer an exit if the economy looks better. The corollary is that asset prices should then be able to stomach the headwinds caused by rising risk premia. Except that I have my doubts that good news in a market that’s near historic highs will compensate sufficiently for the headwinds of common sense. Let me be clearer: I’m concerned that even if, say, earnings improve, equity prices are at risk as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios compress. Similarly, even if default rates don’t jump, bonds could fall.
And why do I say ‘headwinds of common sense’? That’s because the markets are historically a risky place to be in. It’s just of late that equity prices have risen on the backdrop of ever greater complacency (lower volatility). In such an environment, investors are chasing performance unaware of the risks they are taking on. Such investors are referred to as “weak hands” – they will be quick to jump ship when the going gets rough. And don’t think most will get out at the top, as investors have been conditioned to buy the dips. To me, it is no question that volatility – read fear – will come back. The question only is can current asset prices withstand fear?
Similarly, I hear folks arguing we shouldn’t be afraid of higher rates, as rates will only go up as the economy improves. In my assessment, Yellen has all but promised us to be late in raising rates. I can see her move nominal interest rates a little higher; but on a real basis, i.e. after inflation, I very much doubt we will see higher rates. Think about how interests are aligned when both government and consumers have too much debt? They both benefit from higher inflation, i.e. debasing the value of the debt. Who is losing out? Foreigners holding US debt may well be on the losing end of this battle. As foreigners don’t vote, their opinion may matter little.
If you are a consumer with savings rather than debt, be aware that your government’s interests are not aligned with your interests. Don’t count on the government to protect the purchasing power of your savings. Just keep in mind that during the past 100 years when government debt was generally much lower, the greenback lost over 96% of its purchasing power (as measured by the CPI). Differently said, if you are not concerned, you are not paying attention.
Instability the New Normal?
But if a crisis can be priced in, so should be a risky environment, right? It all depends on where one is coming from and where one is heading. We are coming from a highly complacent environment, but are heading towards one that may be ever less stable. I’ve already discussed rising risk premia that should be part of the normalization process. But my negative sentiment extends further.
When I raise my concerns, skeptics point out that the financial system as a whole is a lot more robust now. That’s correct in some ways, but has come at a high price: the destruction of the social fabric and political disintegration. By reflating asset prices, those holding assets disproportionally benefit, increasing the wealth gap. Indeed, I would argue policies of the Fed have a far greater impact on wealth distribution than the policies of Republicans or Democrats. Those that know how to deal with easy money, such as hedge funds, can do great in this environment; however, those that don’t know how to deal with debt easily fall through the cracks, unable to recover.
This isn’t just a U.S. problem. Citizens in large parts of the world are dissatisfied with their political leadership. The reason, in my assessment, is that they have seen their purchasing power decline. In my analysis, when citizens see their purchasing power erode over longer periods, they veer towards more populist politicians and explain:
• The rise of the Tea Party and Occupy Wall Street movements in the U.S.;
• Uprisings in the Middle East; • A populist Prime Minister in Japan; and, amongst others,
• The rise of populist parties in Europe.
Folks in the Middle East start revolutions because they can’t feed themselves anymore as food and energy prices have risen. These trends have come on the backdrop of excessive government debt. Ukraine’s problem is that they can’t balance their books; for now, they have the European Union take over from Russia subsidizing Ukraine. Politicians the world over have in common that they rarely ever blame themselves for the plight of their own people. They tend to blame the wealthy, a minority or foreigners.
To put it bluntly, there’s a reason the Great Depression ended in World War II. We don’t predict World War III is about to break out, but the aftermath of a credit bust is a fertile environment for the sort of dynamics that can lead to armed conflict. Russia has an interest in an unstable Ukraine; Japan might ramp up military spending to boost domestic growth, to name but two sources of instability. The U.S., a superpower no longer able to finance all of its commitments is not exactly a source of stability, either: the biggest threat to U.S. national security may not be China or Russia, it’s the national debt.
As the social fabric in the U.S. erodes, I believe we will elect more populist politicians, making it unlikely that we will come up with major entitlement reform to make deficits sustainable. I was dismayed by Janet Yellen’s testimony last week in which she was either evasive or ignorant about the cost of financing U.S. deficits as rates rise. If she was evasive, she missed a major opportunity to try to foster a national debate. While she provided lip service to the fact that costs will rise as rates move up, she failed to say that if we were to move back to historic rates, we could spend $1 trillion more a year a decade from now servicing the national debt (that’s based on CBO projections and historic levels of interest rates). If she is ignorant of the numbers, I’m no less concerned. Either way, though, odds are the Fed may try to keep borrowing costs low, making the discussion irrelevant. It’s in this context that I believe real interest rates will stay low for a long time, as I don’t think we can afford positive real interest rates for any extended period. This is the key reason why I like gold as an investment, as low to negative real interest rates may make the shiny metal that pays no interest (but cannot be easily ‘printed’) a formidable asset.
To summarize:
• Asset prices are at or near record levels;
• Fear appears almost absent from the markets, complacency near record levels;
• Political instability is on the rise as governments drown in debt.
The first two attributes alone should encourage investors to consider rebalancing their portfolios, taking chips off the table.
But where to hide? Historically, bonds or cash are preferred hiding places; even as bonds have performed just fine of late, I can’t help but be concerned bonds might be one of the worst investments over the next decade. I don’t advocate shorting bonds (it can be very expensive to short bonds as interest is to be paid rather than received), but rather consider shorting the dollar should real interest rates continue to be negative. Broadly speaking, buying anything with one’s dollars is akin to shorting dollars. But one can be specific by buying precious metals; one can diversify to baskets of currencies, possibly be tactical in an effort to stay a step ahead as currency wars may be raging; or one goes up the risk ladder to, say, buy equities. Indeed, equities have performed well relative to cash; but as I think I make very clear in this analysis here, I’m afraid investors buying equities now may be late to the party.
The bad news is that there’s no silver bullet, as there may be no such thing anymore as a ‘safe’ asset. The good news is that many investors could benefit from stress testing their portfolio. If you haven’t done so, make sure you sign up for this free newsletter as we explain how you can get your portfolio stress tested in an upcoming analysis. Also, for more detail on how this may play out, make sure to attend our free Webinar, today, Thursday, July 24, at 4:15pm ET. Please share this newsletter with your friends.
Axel Merk
Axel Merk is President and Chief Investment Officer, Merk Investments,
Manager of the Merk Funds.
 “Mining is an inherently difficult business,” Adrian Day, CEO of Adrian Day Asset Management, told investors at this week’s Sprott Vancouver Natural Resource Symposium. Of course, mining companies, be they senior or junior, run into problems – which if we are being honest are mostly due to money.
“Mining is an inherently difficult business,” Adrian Day, CEO of Adrian Day Asset Management, told investors at this week’s Sprott Vancouver Natural Resource Symposium. Of course, mining companies, be they senior or junior, run into problems – which if we are being honest are mostly due to money.
During his presentation, Day weighed out some of the ups and downs of senior and junior gold companies highlighting some differences, but also some similarities. By looking at both sides of the coin, investors can have a better understanding of the companies that they are investing in.
Apart from cash costs or operating costs, Day highlighted one very significant aspect of the mining industry that affects all producing companies: replacing ounces mined.
“If you look at the production of gold over the course of the bull market, where gold has gone from $200 per ounce to $1,300 per ounce (with a stop at $1,900 along the way), one would think that people would have found and produced more ounces,” Day said.
Unfortunately, that is not the case. For a company like Barrick Gold (TSX:ABX,NYSE:ABX), which mines some 7 million ounces of gold per year, finding a deposit to replace those ounces is no easy task. In fact, Day explained that despite gold’s price increase, the truth is that it’s difficult to find and produce more gold.
So for companies like Barrick, the only solution for replacing depleted reserves is acquisition. The problem with this strategy — although it’s a very good one — is that major mining companies, as Day put it, “do not buy things when things are cheap.”
Essentially, major companies tend to replace their assets when costs and premiums are higher, leading them to acquire debt. The reason they do that, said Day, is that they tend to follow the herd and do as their shareholders request. The flip side is that when the market isn’t doing so well, and investors want to know the reason for such companies’ poor performance, the companies will cut costs, putting assets up for sale and even cutting dividends.
On the exploration side, there are also problems. The biggest of those, as Day explained, are the long odds.
“Only 1 in 5,000 anomalies actually becomes a deposit. Only 1 in 10,000 prospects becomes a major deposit of over 4 million ounces,” Day said. “Those are amazingly long odds, and you obviously can’t succeed by just randomly buying prospects.”
Another problem that Day sees impacting the junior market is money — or rather, a lack thereof. Because exploration companies have no revenue, they need to raise money. That means that it makes no difference whether the market is good or bad: exploration companies need to raise capital.
So why invest?
Looking at gold companies — both major and junior — under the harsh light of day does not make them seem like a good investment. But fret not — Day insisted that “gold stocks can produce outsized returns.”
“If you look at the mining companies today relative to the price of gold, you can see that they are selling at multi-decade lows relative to bullion,” Day said, which is a great opportunity.
Now, if you believe that, then only one question remains: what do you buy?
As Day explained, senior, mid-tier and junior miners do well at different times, with the majors generally performing well early on.
“When the price of gold starts to move and people start getting attracted to gold mining companies, what do they buy? They buy the names they know. And they tend to be for big mining companies,” Day noted.
But when weighing out whether to invest in a major or junior, Day was pretty clear. He commented, “I wouldn’t want anyone to make a mistake that senior mining companies are good investments or that they are less risky than junior mining companies.” So how does one navigate these murky waters?
Well, for Day, that answer comes in two words: business models.
“I think that it is important is to look very selectively at this business,” Day said, adding, “I prefer looking at the business model that mitigates risk.”
In terms of seniors, Day looks for the royalty business model, which can be found at large companies like Franco-Nevada (NYSE:FNV) or at smaller companies like Callinan Royalties (TSXV:CAA) and Altius Minerals (TSX:ALS).
“I think it’s fair to say that by and large most of these companies are not the tremendous bargain basement bargains that the mining companies are, but they are by and large stronger companies with much less risk and much better business models,” he noted.
On the exploration side, just like Rick Rule, Day looks at companies that have adopted the prospect generator model. ”Prospect generators typically use other people’s money to do the risky exploration and are in a much better position to preserve their balance sheets,” he explained.
But in the end, it really is about managing risk and realizing that volatility is the nature of the market.
For more insights from Sprott Global Resource Investments, sign up for the free Sprott’s Thoughts newsletter.
Securities Disclosure: I, Vivien Diniz, hold no investment interest in any of the companies mentioned.
Related reading: